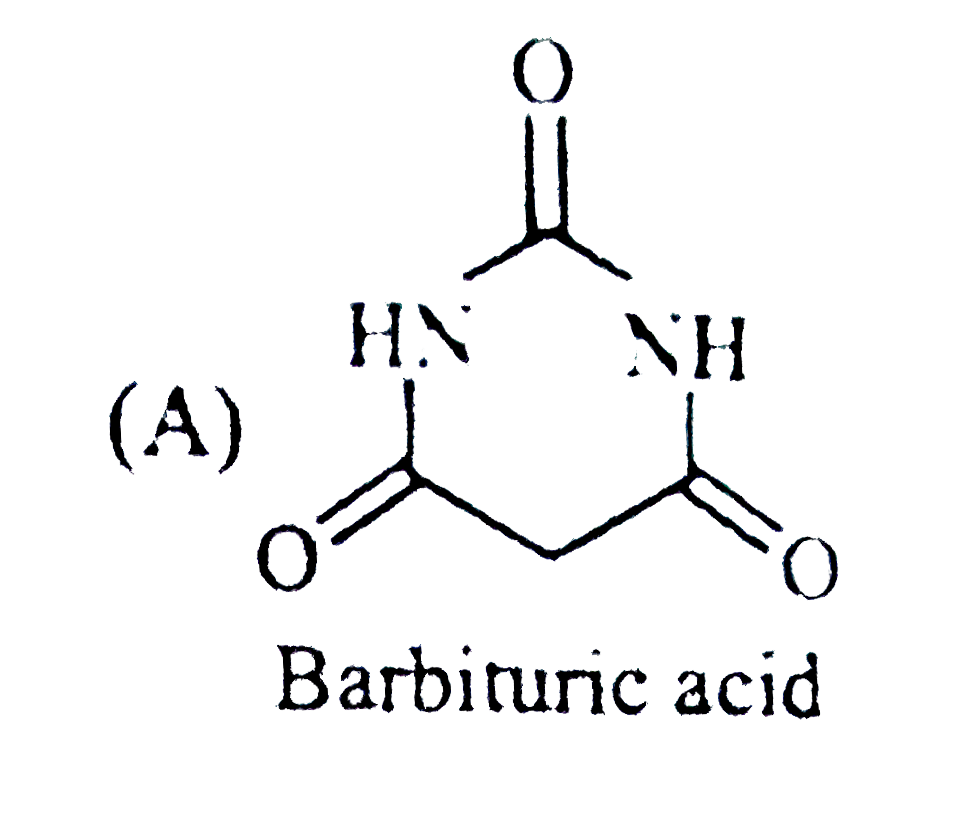
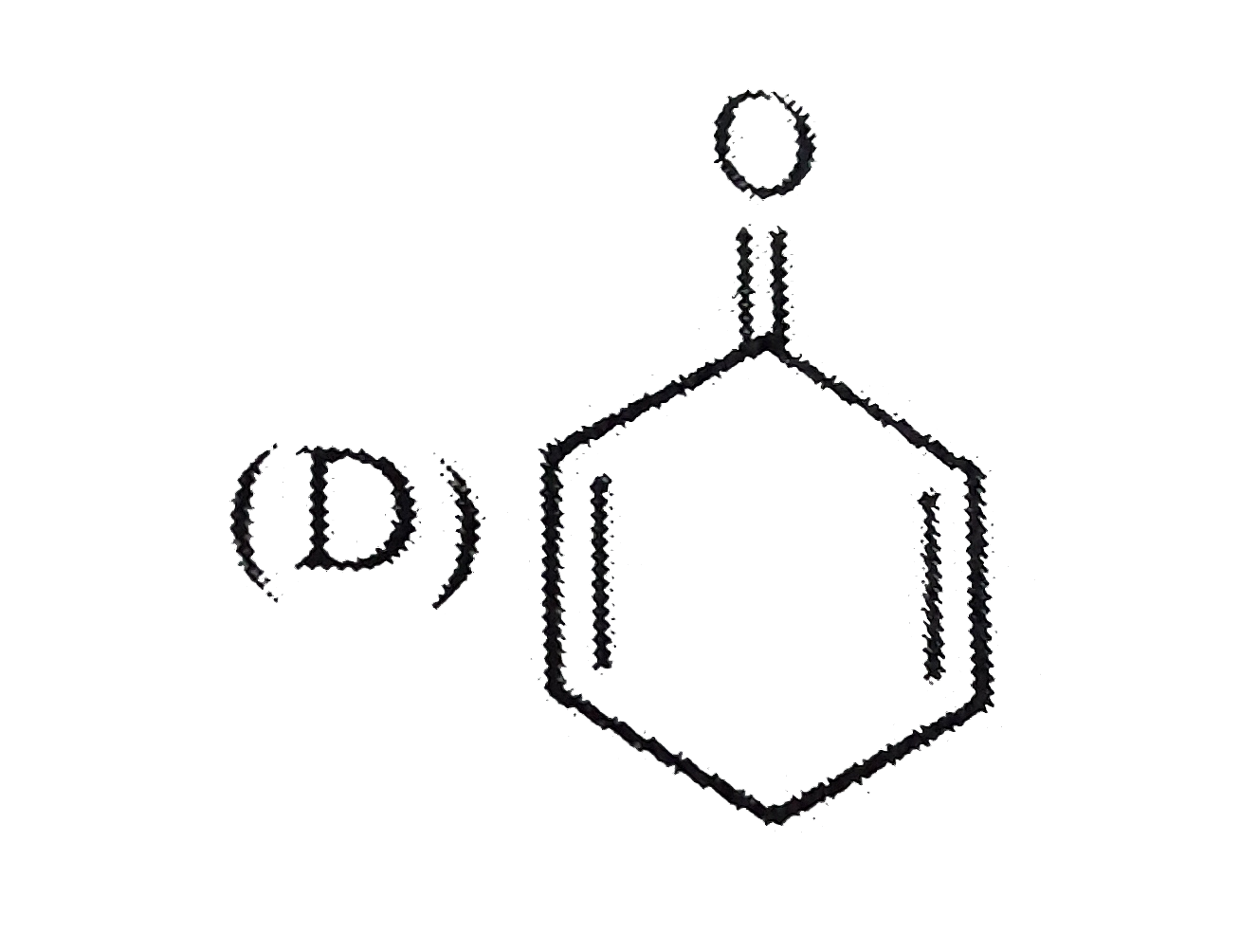
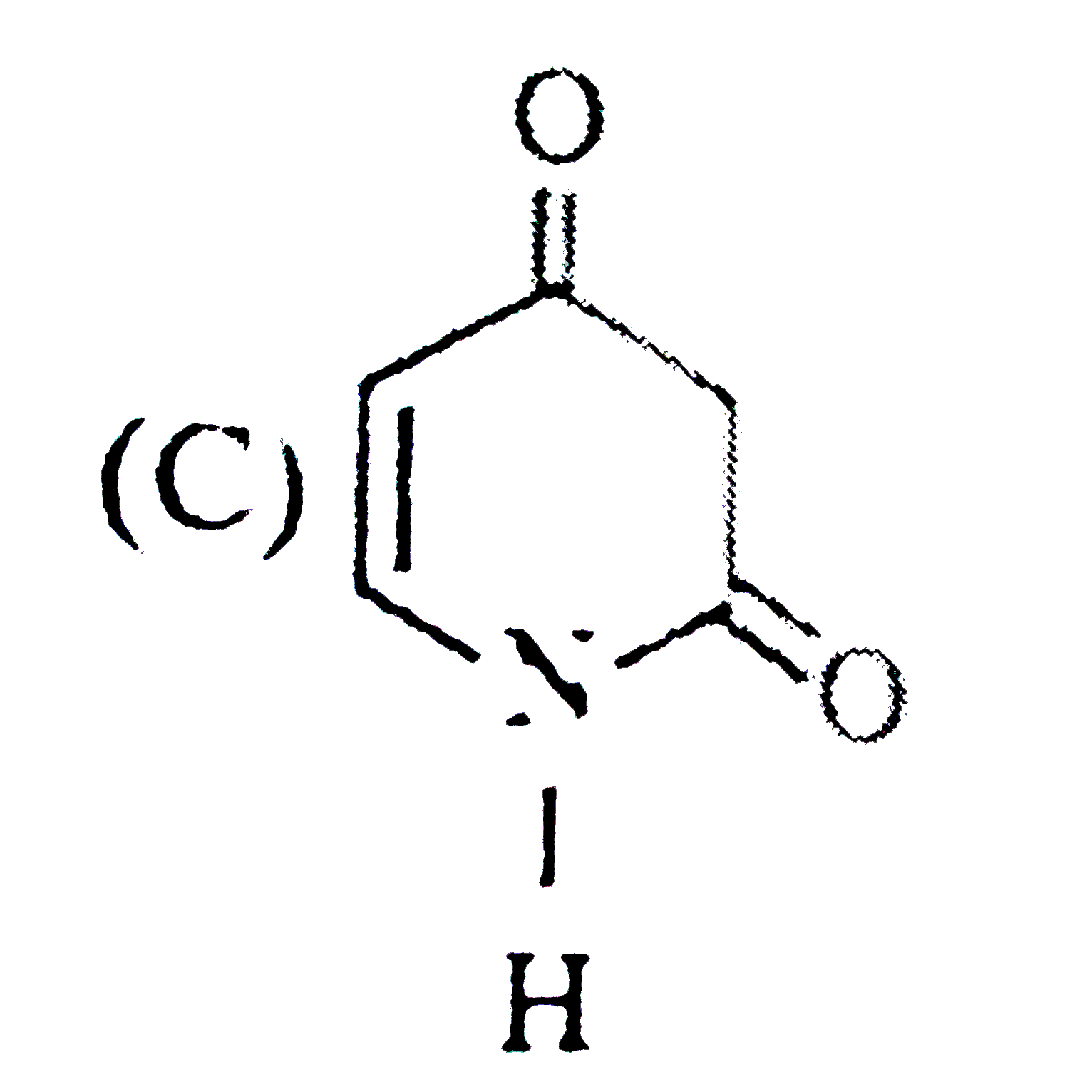A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ACIDIC STRENGTH & BASIC STRENGTH
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise IV|30 VideosACIDIC STRENGTH & BASIC STRENGTH
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise V|16 VideosACIDIC STRENGTH & BASIC STRENGTH
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise II|15 VideosCONCENTRATION TERMS
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise Jee-Advance|3 VideosAIIMS 2019
ALLEN|Exercise CHEMISTRY|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-ACIDIC STRENGTH & BASIC STRENGTH-Exercise III
- In given reaction gas liberated is/are
Text Solution
|
- Arrange marked atom in decreasing order of acidic strength
Text Solution
|
- Compound which can give effevescences with NaHCO(3) .
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: For the given two compounds-I is more acidic than compoun...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: And Statement-2: Lone pair electrons on nitrogen in co...
Text Solution
|
- Match column-I with column-II. .
Text Solution
|
- Match Column-I with column-II
Text Solution
|
- Observe the following feasible reaction: Q. Which of the followin...
Text Solution
|
- Observe the following feasible reaction: Q. Which of the followin...
Text Solution
|
- Observe the following feasible reaction: Q. Identify the feasible...
Text Solution
|
- identify the non-feasible reaction.
Text Solution
|
- Select the number of compounds in which deprotonation gives aromatic a...
Text Solution
|
- Q. identify salt 'A'?
Text Solution
|
- Q. Identify compound 'C'?
Text Solution
|