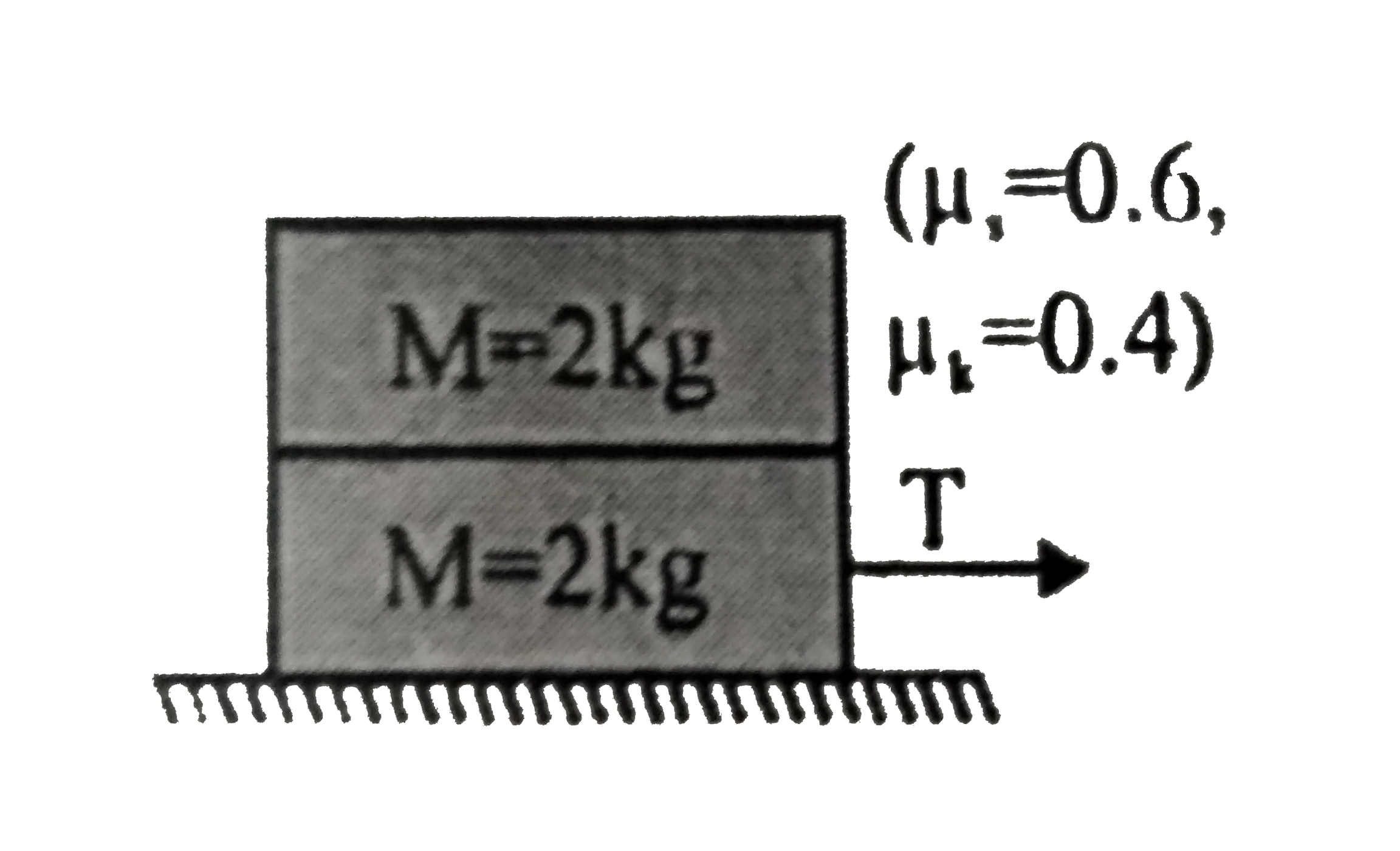
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION & FRICTION
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE (O-1)|51 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION & FRICTION
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE (O-2)|31 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION & FRICTION
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE (S-1)|23 VideosMOTION IN A PALNE
ALLEN|Exercise SOLVED EXAMPLE|28 VideosNEWTONS LAWS OF MOTION
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-III|28 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION & FRICTION-EXERCISE (S-2)
- A ladder is hanging from ceiling as shownin figure. Three men A, B and...
Text Solution
|
- A box of mass m is placed on a smooth horizontal platform as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- Tow men of masses m(1)and m(2) hold on the opposite ends of a rope pas...
Text Solution
|
- The system shown in the figure is initially in equilibrium. A is of ma...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the following figures, block of mass 2 kg is in equilibriu...
Text Solution
|
- A 2 kg block A is attached to one end of a light string that passes ov...
Text Solution
|
- The coefficient of static and kinetic friction between the two blocks ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure masses m(1),m(2) and M are kg. 20 Kg, 5 kg and 50 kg res...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown the acceleration of A is, bara(A)=(15hati+15hatj)m...
Text Solution
|