Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-CHEMICAL KINETICS-Numerical Problems
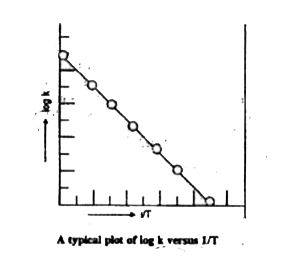
- How is rate constant of a reaction related to its activation energy?
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant of a reaction is 1.5 xx 10^7 sec^(-1) at 50^@C and 4...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for the decomposition of N2O6, N2O6 rarr N2O4+1/...
Text Solution
|
- The first order rate constant for the decomposition of ethyl iodide by...
Text Solution
|
- The three fourth of a first order reaction is completed in 32 minutes....
Text Solution
|
- 60% of a first order reaction was completed in 60 minutes. When was it...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction is 75% complete in 60 min. Find the half-life o...
Text Solution
|
- Ammonia and oxygen react at high temperature as : 4 NH (3)(g) to 4NO (...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction 2 N (2) O (5) (g) to NO (2) (g) + O (2) (g) takes place i...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction 3X rarr 2Y+Z procees in a closed vessel. The rate of disapp...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction is 50% complete in 69.3 minutes. Calculate the ...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction is 20% complete in the 10 minutes. Calculate th...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction is 15% complete in 20 minutes. How long will it...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction is 20% complete in the 10 minutes. Calculate th...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction is 15% complete in 20 minutes. How long will it...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction is 40% complete in 50 minutes. In what time wil...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for the first order reactior becomes three times whe...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for a first order reaction becomes six times when th...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for a first order reaction becomes six times when th...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction : N (2) + 3H(2) to 2 NH (3) The rate of reaction meas...
Text Solution
|
- The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in the presence of iodide ion h...
Text Solution
|