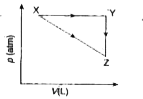
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise LEVEL-II (Assertion-Reason Type)|18 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTION (LEVEL -ll)|42 VideosCLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTIONS (LEVEL-III ( Linked Comprehension Type ))|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION-CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS -LEVEL-III
- Which is not correct relationship between Delta G^(Ө) and equilibrium ...
Text Solution
|
- The following is(are) endothermic reaction(s)
Text Solution
|
- For an ideal gas, consider onlyp-V work in going from an initial state...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure =p(1...
Text Solution
|
- For the C(s) + H (2) O (g) to CO (g) + H (2) (g ) reaction, Delta H ^(...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following sets show the intensive properties?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are endothermic processes?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the options given below are correct?
Text Solution
|
- Enthalpy change equals internal energy change for a chemical reaction ...
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy of fusion of ice is 6.02 kJ mol^(-1). The heat capacity o...
Text Solution
|
- Temperature of one mole of helium gas is increased by 1^(@)C. Hence, t...
Text Solution
|
- 4.48 Lofan ideal gas at S.T.P requires 12 calories to raise its temper...
Text Solution
|
- The polymerisation of propene to linear polypropene is represented by ...
Text Solution
|
- The lattice energy of solid KCI is 181 kcal mol^(-1) and the enthalpy...
Text Solution
|
- A heated iron block at 127^(@)C loses 300 J. of heat to the surroundin...
Text Solution
|
- What work is to be done on 2 mole of a perfect gas at 27^(@)C if it is...
Text Solution
|
- The heat of neutralisation of oxalic acid is -25.4 kcal mol^(-1) using...
Text Solution
|
- 100 mole of an ideal gas at 8.21 atm is heated to show a linear graph ...
Text Solution
|
- match the following
Text Solution
|