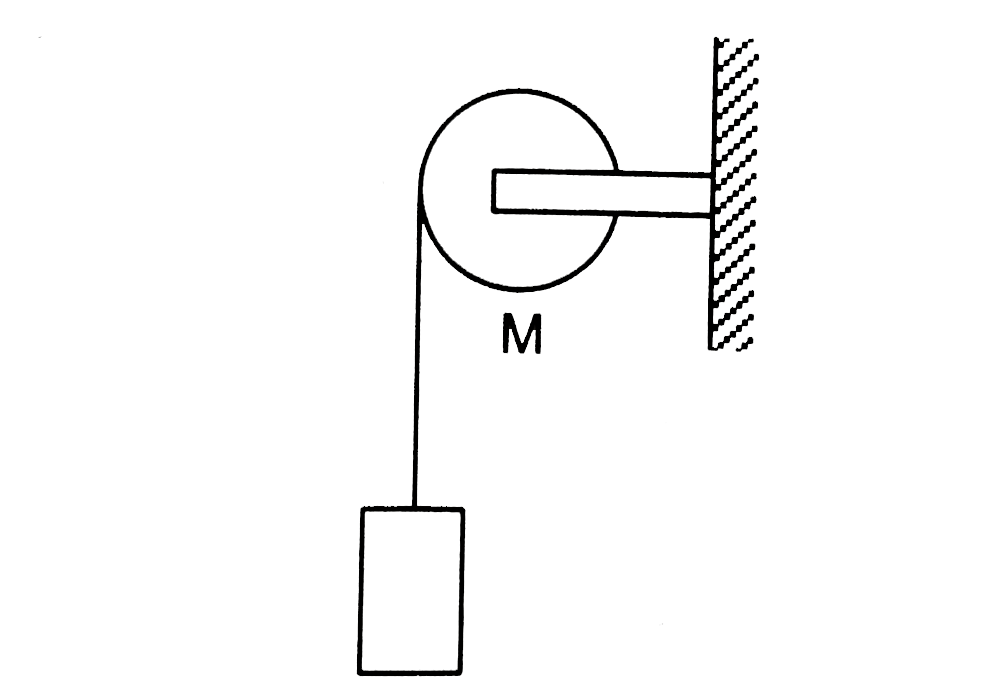Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-ROTATIONAL MECHANICS-Exercises
- Consider a pulley fixed at its centre of mass by a clamp. A light rope...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel is making revolutions about its axis with uniform angular acce...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel rotating wilth unifrom angular acceleration covers 50 revoluti...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel starting from rest is uniformly accelerate at 4 rad /s^2 for...
Text Solution
|
- A body rotates about a fixed axis with an angular acceleration of 1 ra...
Text Solution
|
- Find the angular velocity of a body rotating with an acceleration of 2...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius 10 cm is rotating about its axis at an angular speed...
Text Solution
|
- A disc rotates about its axis with a constant angular acceleration of ...
Text Solution
|
- A block hangs from a string wrapped on a disc of radius 20 cm free to ...
Text Solution
|
- Three particles, each of mass 200 g are kept at the corners of an equi...
Text Solution
|
- Particles of masses 1g, 2g, 3g ….100g are kept at the marks 1cm, 2cm, ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the moment of inertia of a pair of spheres, each having a mass m ...
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a uniform rod of mass 0.50 kg and length 1 m ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the radius of gyration of a circular ring of radius r about a lin...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of gyration of a uniform disc about a line perpendicular to...
Text Solution
|
- Find the moment of inertia of a uniform square plate of mass M and edg...
Text Solution
|
- The surface density (mass/area) of a circular disc of radius a depends...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is projected with speed u at an angle theta with ...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of length l is pulled aside to make an angle theta w...
Text Solution
|
- When a force of 6.0 N is exerted at 30^@ to a wrench at a distance of ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the total torque acting on the body shown in figure about th...
Text Solution
|