Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-EXERCISE
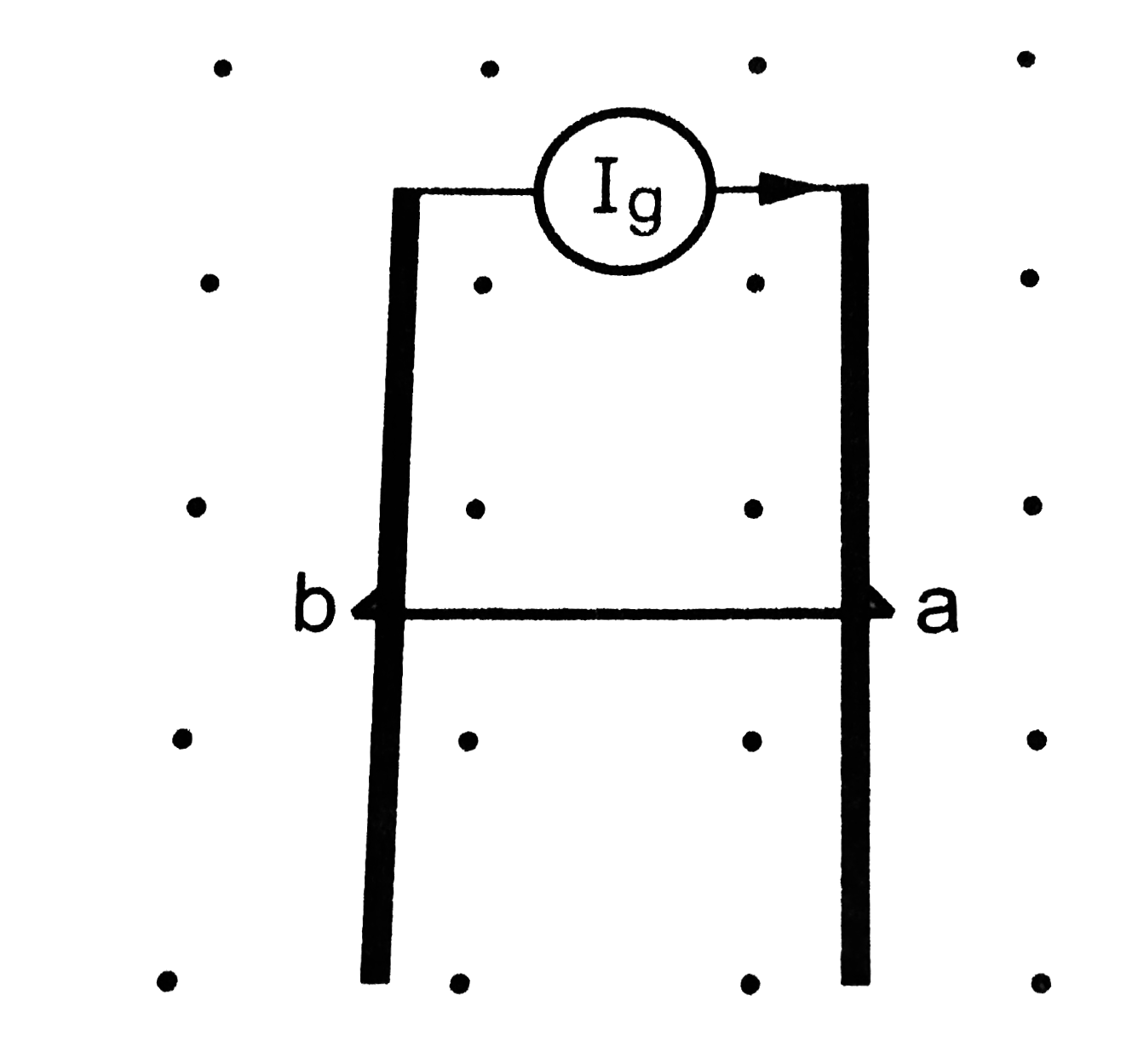
- The current generator I g, shown in . Sends a constant current I throu...
Text Solution
|
- The current generator ig, shown in , sends a constant current I throu...
Text Solution
|
- The system containing the rails and the wire of the previous problem i...
Text Solution
|
- The rectangualr wire- frame, shown in has a width d, mass m, resist...
Text Solution
|
- Shows a smooth pair of thick metallic rails connected across a battery...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire ab of length l, resistance r and mass m starts slidi...
Text Solution
|
- A bicycle is resting on its stand in the east - west direction and the...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting disc of radius r rotaes with a small but constant angul...
Text Solution
|
- shows a conducting disc rotating about its axis in a perpendicular ma...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field inn a region is given by vec B = veck (B0)/(L) y wh...
Text Solution
|
- shows a straight, long wire carrying a current I and a rod of length l...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a situation similar to that of the previous problem except th...
Text Solution
|
- Shows a square frame of wire having a total resistance r placed coplan...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular metallic loop of length l and width b is placed coplan...
Text Solution
|
- Shows a conducting circular loop of radius a placed in a uniform, perp...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in the figure of the previous problem. Su...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a variation of the previous problem. Suppose the circular loo...
Text Solution
|
- Shows a situation similar to the previous problem. All parameters are...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of mass m and length l can slide freely on a pair of smooth, ve...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field B exists in a cylindrical region, shown dotte...
Text Solution
|