Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-EXERCISE
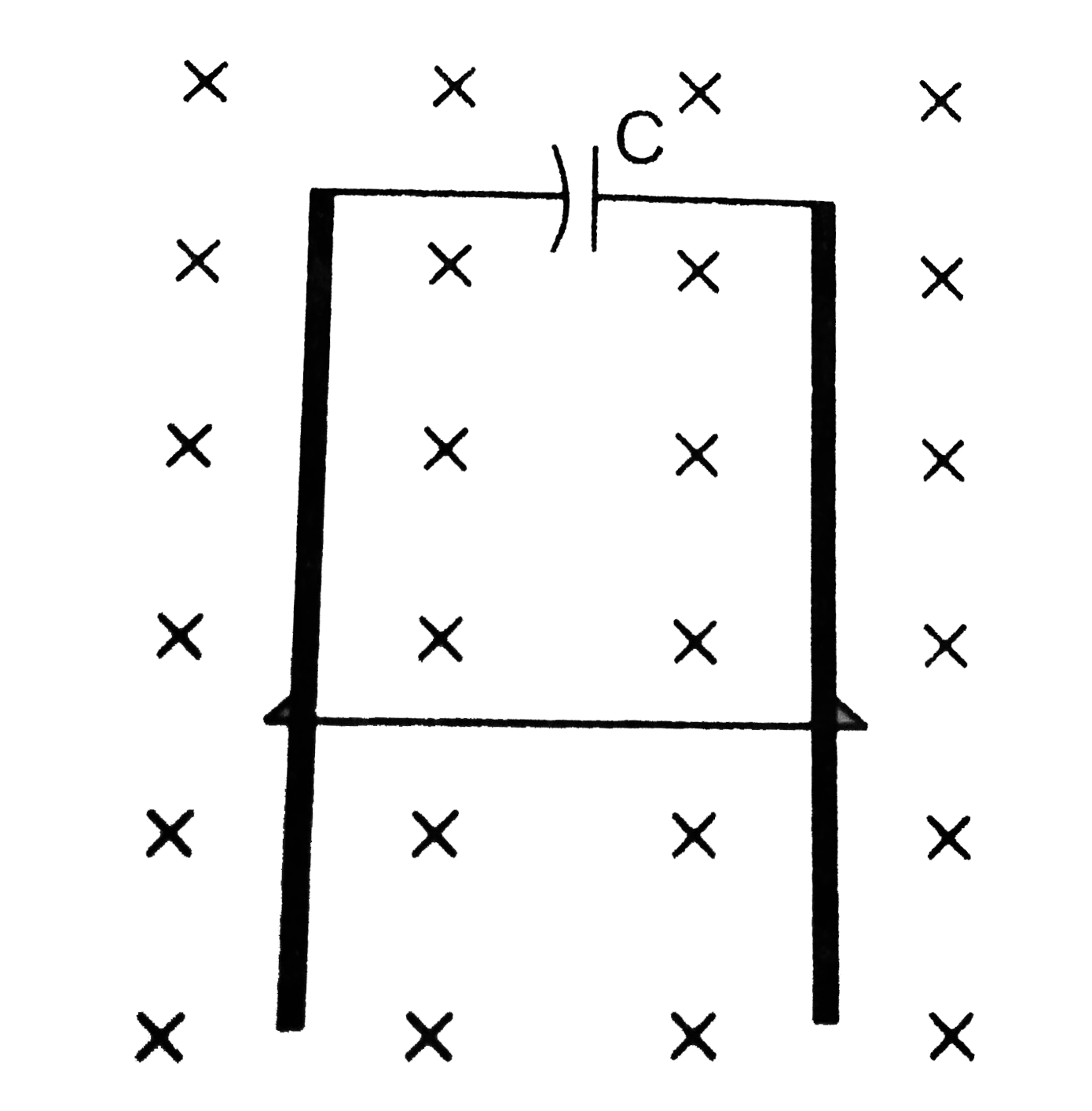
- Consider a variation of the previous problem. Suppose the circular loo...
Text Solution
|
- Shows a situation similar to the previous problem. All parameters are...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of mass m and length l can slide freely on a pair of smooth, ve...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field B exists in a cylindrical region, shown dotte...
Text Solution
|
- The current in an ideal, long solenoid is varied at a uniform rate of...
Text Solution
|
- An average emf of 20 V is induced in an inductor when the current in...
Text Solution
|
- A magnetic flux of 8X10^(-4) weber is linked with each turn of a 200 -...
Text Solution
|
- The current in a solenoid of 240 turns, having a length of 12 cm and ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the value of t/tau for which the current in an LR circuit builds ...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor coil carries a steady state current of 2.0 A when connect...
Text Solution
|
- A coil having inductance 2.0 H and resistance 20 Omega is connected t...
Text Solution
|
- A coil of resistance 40 Omega is connected across a 4.0 V battery. 0...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor of inducance 5.0 H, having a negligible resistance, is con...
Text Solution
|
- The time constant of an LR circuit is 40 ms. The circuit is connected...
Text Solution
|
- An LR circuit has L = 1.0 H R =20 Omega. It is connected across an e...
Text Solution
|
- What are the values of the self induced emf in the circuit of the pr...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor-coil of inductance 20 mH having resistance 10 Omega is jo...
Text Solution
|
- An LR circuit constains an inductor of 500 mH, a resistor of 25.O Om...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor coil of resistance 10 Omega and inductance 120 mH is conn...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor coil of inductance 17 mH is constructed from a copper wire...
Text Solution
|