Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-NTA TPC JEE MAIN TEST 47-PHYSICS (SUBJECTIVE NUMERICAL)
- The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted from a metal surf...
Text Solution
|
- In the above figure, the truth table for a logic gate at some instant ...
Text Solution
|
- Given a 3.3 xx 10^(-27) Kg of hydrogen gas with root mean square speed...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is wrapped N times over a solid sphere of mass m which is place...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the phase difference introduced by a quartz plate of thickne...
Text Solution
|
- In the above figure, two blocks of masses 5 kg & 1 kg are connected by...
Text Solution
|
- If The density of wood in C. G. S system is 0.5 g cm^(-3). If the corr...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform capillary tube of length l and inner radius r with its upper...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mole of monoatomic gas initially at 927^(@)C undergoes a Carnot cycl...
Text Solution
|
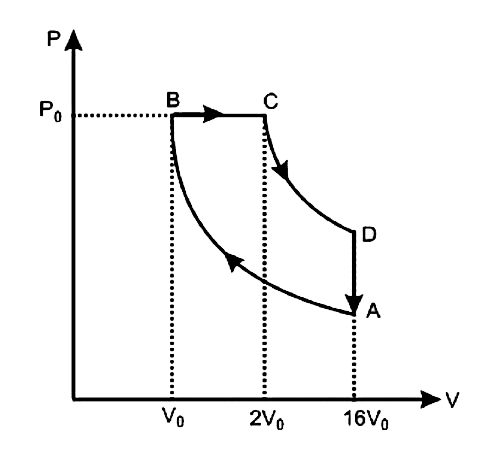
- One mole of a diatomic ideal gas (gamma=1.4) is taken through a cyclic...
Text Solution
|