A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
EDUCART PUBLICATION-SAMPLE PAPER 9 -SECTION - C
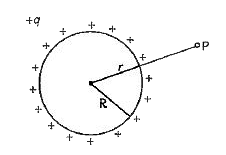
- Electric field intensity' at point P due to 'charge distributed over ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure charge on capacitor C2 is:
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the figure, four bulb consume same power. The resistance o...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic field vecB is produced by a current. On the basis of this con...
Text Solution
|