Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MODEL PAPER 9
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise SECTION-C|6 VideosMODEL PAPER 9
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise SECTION-C|6 VideosMODEL PAPER 8
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise SECTION-C|11 VideosMOST IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-MODEL PAPER 9-SECTION-B
- Define molarity Calculate the molarity of a solution containing 5g of...
Text Solution
|
- Which metal is present in cinnabar ore?
Text Solution
|
- Which metal is present in Pyrolusite ore?
Text Solution
|
- Define Adsorption. ,Discuss the differences between physical adsorptio...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the purification of sulphide ore by Froth Floatation Method.
Text Solution
|
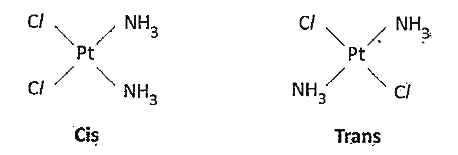
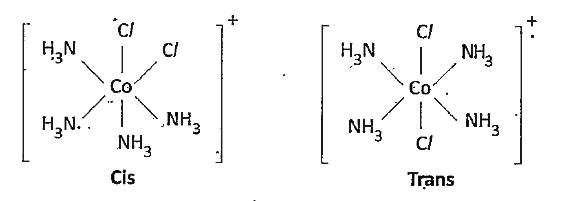
- What is Stereoisomerism ? Explain the geometrical' isomerism in coordi...
Text Solution
|
- Write the formula and structure of Hyposulphurous acid?
Text Solution
|
- Give the sources of the following vitamin and name the diseases cause...
Text Solution
|
- What are analgesics ? How are they classified ?
Text Solution
|