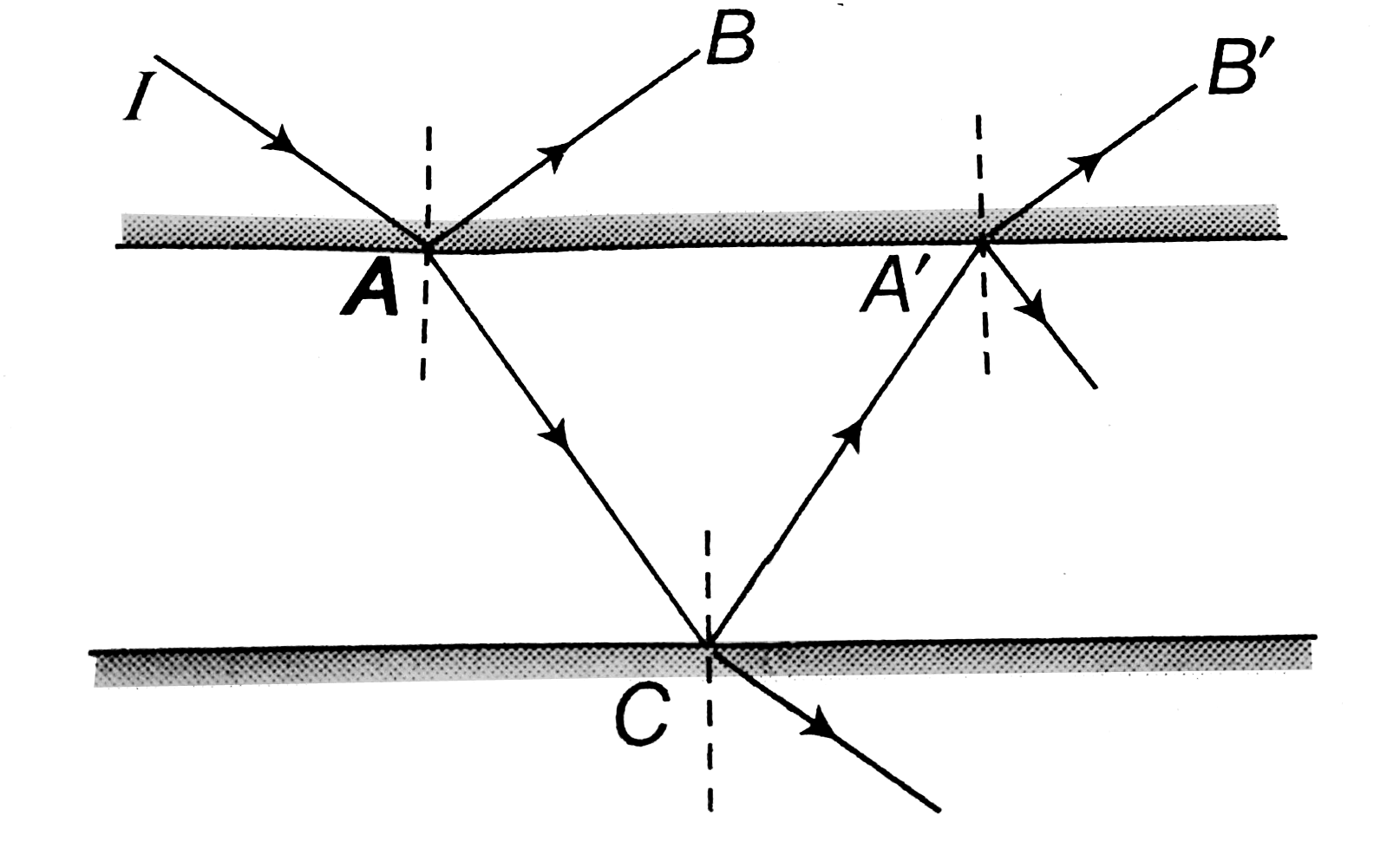
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-NTA TPC JEE MAIN TEST 124 -PHYSICS
- Three very large plates of same area are kept parallel and close to ea...
Text Solution
|
- There is a horizontal cylindrical uniform but time-varying nagnetic fi...
Text Solution
|
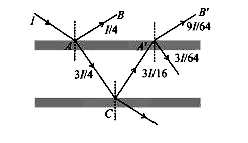
- A ray of light intensity I is incident on a parallel glass-slab at a p...
Text Solution
|
- A manometer connected to a closed tap reads 3.5xx10^(5)N//m^(2).When t...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m kg lifted by a man to a height of one metre in 30 sec...
Text Solution
|
- If M(O) is the mass of an oxygen isotope .(8)O^(17),M(p) and M(n) are ...
Text Solution
|
- In the Young's double slit experiment, the spacing between two slits i...
Text Solution
|
- In a radioactive series, .(92)U^(238) charges to .(82)Pb^(206) through...
Text Solution
|
- The logic circuit shown below has the inputs waveforms A and B as show...
Text Solution
|
- A vibraiton magnetometer consits of two idential bar magnets placed on...
Text Solution
|
- According to Huygens' principle, during rafraction of light from air t...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 V, AC source of frequency 500 Hz is connected to an LCR circuit ...
Text Solution
|
- A car is negotisting a curved road of radius R . The road is banked at...
Text Solution
|
- The amplitude of a simple pendulum is 10 cm. When the pendulum is at a...
Text Solution
|
- A square loop ABCD , carrying a current I, is placed near and coplanar...
Text Solution
|
- Two coherent sound sources A and B produce a sound of wavelength lambd...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitance of 2 muF is required in an electrical circuit across a p...
Text Solution
|
- Visible light of wavelength 6000 xx 10 ^( - 8 ) cm falls no...
Text Solution
|
- The capacitance of the capacitors C(1), C(2) and C(3) are 4muF, 6muF a...
Text Solution
|
- 1.56 × 10^5 J of heat is conducted through is 2 m^2 wall of 12 cm thi...
Text Solution
|