A graph was plotted between molar conductivity of various electrolytes (NaCl, HCl and `NH_4OH`) and `sqrtC` (in mol`L^(-1)`) . Correct set is :
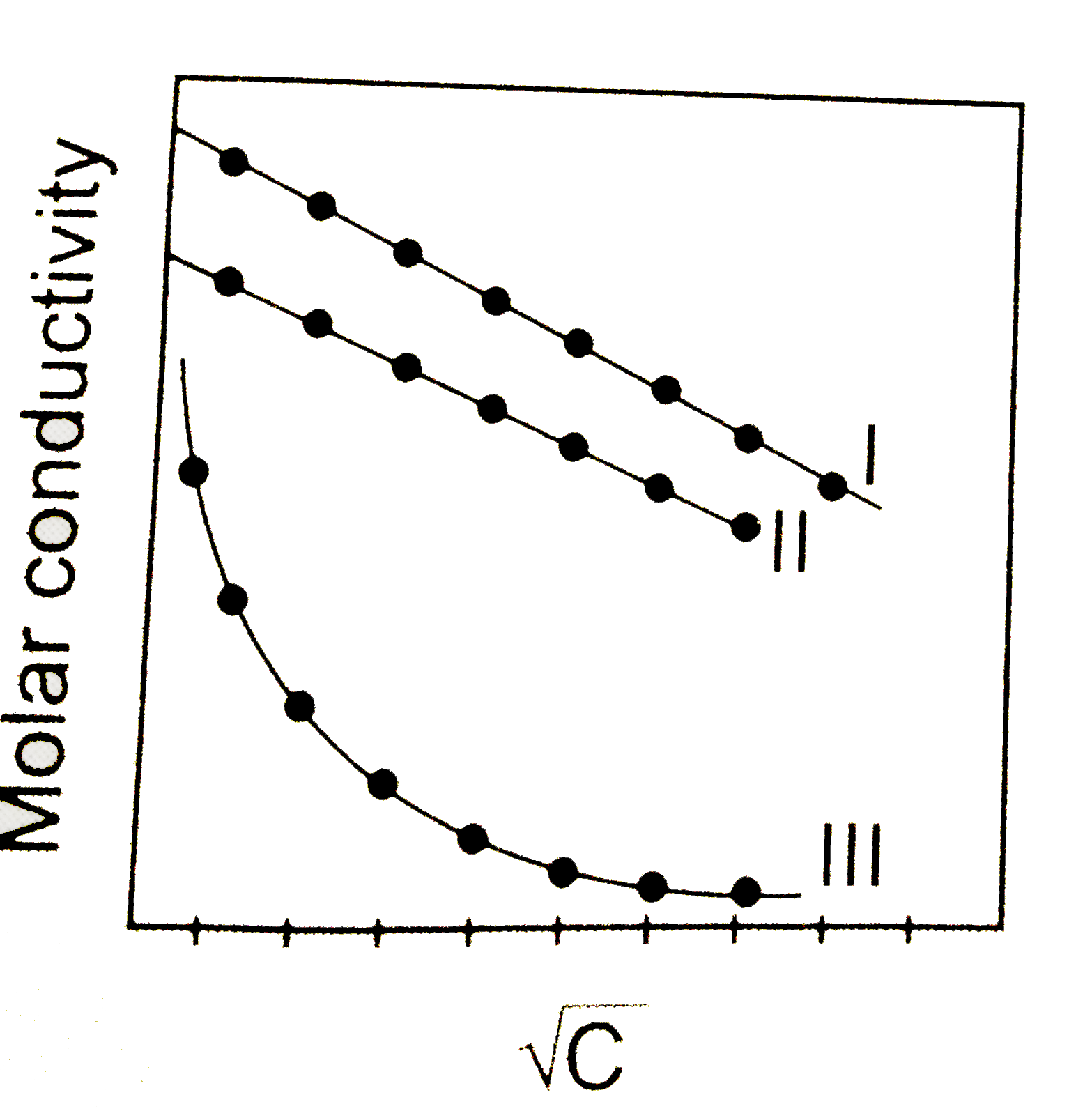
A graph was plotted between molar conductivity of various electrolytes (NaCl, HCl and `NH_4OH`) and `sqrtC` (in mol`L^(-1)`) . Correct set is :


A
I(NaCl),II(HCl) , III(`NH_4OH`)
B
I(HCl),II(NaCl) , III(`NH_4OH`)
C
I(`NH_4OH`), II(NaCl), III(HCl)
D
I(`NH_4OH`), II(HCl) , III(NaCl)
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
B
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
At 25°C the molar conductances at infinite dilution for the strong electrolytes NaOH, NaCl and BaCl_(2) are 248 xx 10^(-4) ,126 xx 10^(-4) and 280xx10^(-4)Sm^(2)mol^(-1) respectively, lambda_(m)^(o) Ba(OH)_(2) in Sm^(2)mol^(-1) is
Resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 mol L^(-1) KCl solution is 100Omega . If the resistacne of the same cell when filled with 0.02 mol L^(-1) KCl solution is 520 Omega , calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 mol L^(-1) KCl solution . The conductivity of 0.1 mol L^(-1) KCl solution is 1.29 S/m.
The limiting molar conductivities (Lambda^(0)) for NaCl, KBr and KCl are 126, 152 and 150 S. cm^(2) "mol"^(-1) respectively. Then A for NaBr is
The conductance of a salt solution (AB) measured by two parallel electrodes of area 100 cm^(2) separated by 10 cm was found to be 0.0001 Omega^(-1) . If volume enclosed between two electrode contains 0.1 mole of salt, and the molar conductivity (S cm^(2) mol^(-1)) of salt at same concentration is 1.0 xx 10^(-x) , x is
Conductors allow the passage of electric current through them. Metallic and electrolytic are the two types of conductors. Current carriers in metallic and electrolytic conductors are free electrons and free ions respectively. Specific conductance or conductivity of the electrolyte solution is given by the following relation: K= cx (l)/(A) where, c=1/R is the conductance and 1/A is the cell constant, Molar conductance (^^_m) and equivalence conductance (^^_e) of an electrolyte solution are calculated using the following similar relations: ^^_m = K xx (1000)/(M) ^^_(e) = K xx (1000)/(N) where, M and N are the molarity and normality of the solution respectively. Molar conductance of strong electrolyte depends on concentration : ^^_m = ^^_m^(0) - b sqrt(C) ^^_m^(0) = molar conductance at infinite dilution C = concentration of the solution b = constant The degrees of dissociation of weak electrolytes are calculated as alpha = (^^_m)/(^^_m^(0)) = (^^_e)/(^^_e^(0)) Which of the following decreases on dilution of electrolytic solution?
Conductors allow the passage of electric current through them. Metallic and electrolytic are the two types of conductors. Current carriers in metallic and electrolytic conductors are free electrons and free ions respectively. Specific conductance or conductivity of the electrolyte solution is given by the following relation: K= cx (l)/(A) where, c=1/R is the conductance and 1/A is the cell constant, Molar conductance (^^_m) and equivalence conductance (^^_e) of an electrolyte solution are calculated using the following similar relations: ^^_m = K xx (1000)/(M) ^^_(e) = K xx (1000)/(N) where, M and N are the molarity and normality of the solution respectively. Molar conductance of strong electrolyte depends on concentration : ^^_m = ^^_m^(0) - b sqrt(C) ^^_m^(0) = molar conductance at infinite dilution C = concentration of the solution b = constant The degrees of dissociation of weak electrolytes are calculated as alpha = (^^_m)/(^^_m^(0)) = (^^_e)/(^^_e^(0)) Which of the following equality holds good for the strong electrolytes?
Conductors allow the passage of electric current through them. Metallic and electrolytic are the two types of conductors. Current carriers in metallic and electrolytic conductors are free electrons and free ions respectively. Specific conductance or conductivity of the electrolyte solution is given by the following relation: K= cx (l)/(A) where, c=1/R is the conductance and 1/A is the cell constant, Molar conductance (^^_m) and equivalence conductance (^^_e) of an electrolyte solution are calculated using the following similar relations: ^^_m = K xx (1000)/(M) ^^_(e) = K xx (1000)/(N) where, M and N are the molarity and normality of the solution respectively. Molar conductance of strong electrolyte depends on concentration : ^^_m = ^^_m^(0) - b sqrt(C) ^^_m^(0) = molar conductance at infinite dilution C = concentration of the solution b = constant The degrees of dissociation of weak electrolytes are calculated as alpha = (^^_m)/(^^_m^(0)) = (^^_e)/(^^_e^(0)) For which of the following electrolytic solution ^^_m and ^^_e are equal ?
The ionization constant of a weak acid is 1.6 xx 10^(-5) and the molar conductivity at infinite dilution is 380 xx 10^(-4) sm^(2) mol^(-1) . If the cell constant is 0.01m^(-1) , then conductance of 0.01M acid solution is