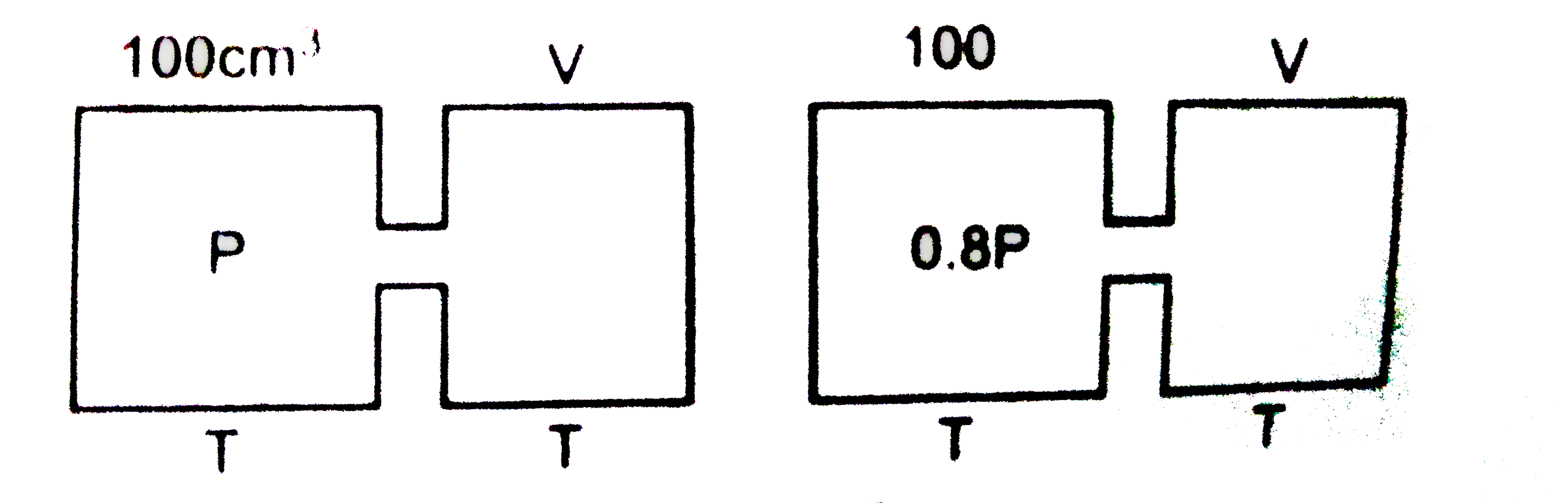A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GASEOUS STATE
NARENDRA AWASTHI|Exercise Level 1 (Q.31 To Q.60)|1 VideosGASEOUS STATE
NARENDRA AWASTHI|Exercise Level 1 (Q.121 To Q.150)|1 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
NARENDRA AWASTHI|Exercise Level 3 - Subjective Problems|1 VideosIONIC EEQUILIBRIUM
NARENDRA AWASTHI|Exercise Assertin-Reason Type Questions|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems