A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-ALKYL HALIDES (SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS)-LEVEL-2
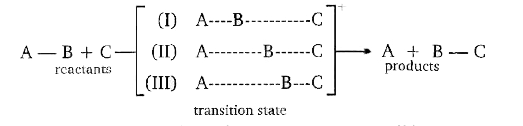
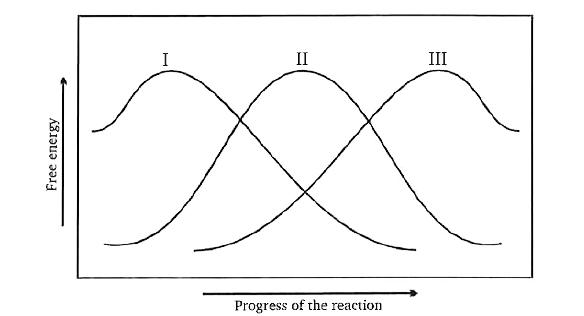
- Transition state 2 is structurally most likely as :
Text Solution
|
- The order of the nucleophilicity of F^(-) ,Cl^(-), Br^(-) and I^(-) in...
Text Solution
|
- Statement - 1 : CH(3) - CH(2) - Cl + NaI("Acetone") rarr CH(3) - CH(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following:
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following: undergoes and S(N^2) reaction m...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following: undergoes and S(N^1) reaction m...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following: undergoes an E2 reaction to giv...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following: reacts with Nal to give (Z) - 1...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following: undergoes and S(N^(1)) reaction...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following : undergoes and S(N^2) reaction ...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following : undergoes an E1 reaction more ...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following : undergoes an S(N^1) reaction m...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following : undergoes an S(N^2) reaction m...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following : undergoes an E2 reaction more ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column :
Text Solution
|
- Matrix :
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following : undergoes an S(N^2) reaction m...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following : undergoes an S(N^1) reaction m...
Text Solution
|
- Encircle whichever of the following : undergoes an S(N^1) reaction m...
Text Solution
|
- Reativity : Circle the reaction that reacts FASTER by S(N^2) in each p...
Text Solution
|
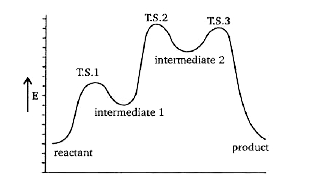
- Consider the potential energy diagram given below (X) Name the po...
Text Solution
|