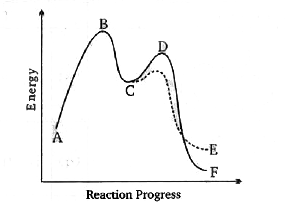A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-ALKYL HALIDES (SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS)-LEVEL-2
- Encircle whichever of the following : undergoes an S(N^1) reaction m...
Text Solution
|
- Reativity : Circle the reaction that reacts FASTER by S(N^2) in each p...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the potential energy diagram given below (X) Name the po...
Text Solution
|
- Select whether the following combinations of reactants will react by s...
Text Solution
|
- Select whether the following combinations of reactants will react by s...
Text Solution
|
- Select whether the following combinations of reactants will react by s...
Text Solution
|
- Select whether the following combinations of reactants will react by s...
Text Solution
|
- Select whether the following combinations of reactants will react by s...
Text Solution
|
- Select whether the following combinations of reactants will react by s...
Text Solution
|
- Select whether the following combinations of reactants will react by s...
Text Solution
|
- Examine the ten structural formulas shown in fig. & select that satify...
Text Solution
|
- Select which reaction from the following reaction pairs will occur fas...
Text Solution
|
- Select which reaction from the following reaction pairs will occur fas...
Text Solution
|
- Select which reaction from the following reaction pairs will occur fas...
Text Solution
|
- Select which reaction from the following reaction pairs will occur fas...
Text Solution
|
- Select which reaction from the following reaction pairs will occur fas...
Text Solution
|
- Tick your answer in the given box.
Text Solution
|
- Match the column :
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|