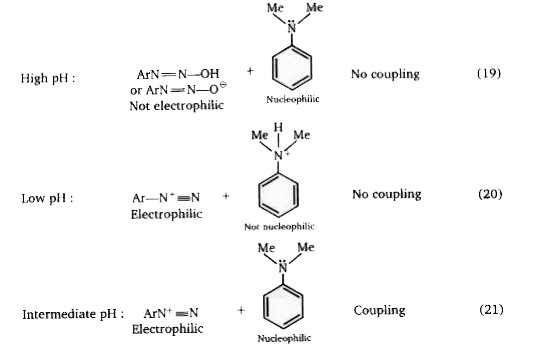
Effect of pH on the coupling reaction : Coupling is best carried out in solutions that are neither too strongly acidic nor alkaline. The reasons for this can be seen if we examine a typical case, the coupling of benzenediazonium chloride with dimethylaniline. At high pH, the diazonium ion is present in very low concentration, since most of it has been converted to ArN =N – OH and `ArN =N-O^-` . Neither ArN = NOH (the diazohydroxide) nor `ArN=N-O^-` (the diazotate ion) is electrophilic, and thus does not couple with the amine. At low pH, the dimethylaniline will be largely protonated to `Ar N^+ Me_2H` , and thus the activating effect of the `-NMe_2` group is destroyed, since the nitrogen atom no longer possesses an unshared pair of electrons: