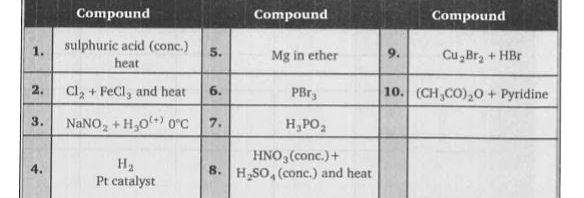
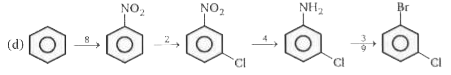
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL-2 (COMPREHENSION)|16 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL-2 (SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS)|3 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL-2 (SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS)|3 VideosAMINES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise Level-2|1 VideosBIOMOLECULES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise LEVEL - 2|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-AROMATIC COMPOUNDS -LEVEL-2
- Each of the six compounds shown at the bottom of the page has two arom...
Text Solution
|
- When given substituents on a benzene ring, as activating or de-activat...
Text Solution
|
- Devise a series of reactions to convert benzene into meta - chlorobrom...
Text Solution
|
- Match the Column (I) and Column (II). (Matrix)
Text Solution
|
- Match the Column (I) and Column (II).
Text Solution
|
- Match the Column (I), Column (II) and Column (III). (Matrix)
Text Solution
|
- Match the Column (I), Column (II) and Column (III). (Matrix)
Text Solution
|
- Among the following compound.
Text Solution
|
- Of the following compounds which will react with Br2 at room temperat...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following compound.
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following table.
Text Solution
|