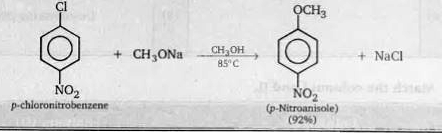
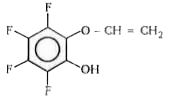
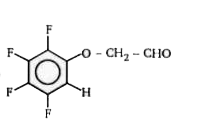
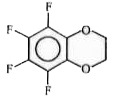
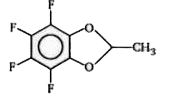
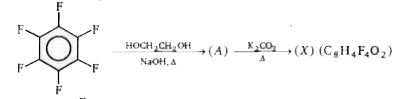A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-AROMATIC COMPOUNDS -LEVEL-2 (COMPREHENSION)
- Given is the energy profile diagram of nitration of benzene using mix...
Text Solution
|
- Given is the energy profile diagram of nitration of benzene using mix...
Text Solution
|
- Given is the energy profile diagram of nitration of benzene using mix...
Text Solution
|
- Examine the ten structural formulas shown below and select those that ...
Text Solution
|
- Examine the ten structural formulas shown below and select those that ...
Text Solution
|
- Nitrobenzene is a versatile compound that may be converted into a wide...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I and II.
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I and II.
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic Aromatic substitution (SN(Ar)) : A substituted benze...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic Aromatic substitution (SN(Ar)) : A substituted benze...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic Aromatic substitution (SN(Ar)) : A substituted benze...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic Aromatic substitution (SN(Ar)) : A substituted benze...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic Aromatic substitution (SN(Ar)) : A substituted benze...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic Aromatic substitution (SN(Ar)) : A substituted benze...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic Aromatic substitution (SN(Ar)) : A substituted benze...
Text Solution
|
- Identify product (A) and write its structure.
Text Solution
|