Esterification (shown below) is a reaction converting a carboxylic acid toits ester. Itinvolves only the carbonyl carbon. Esterification of (-) -lactic acid with methanol yields (+)-methyl lactate. Assuming that there are no side reactions, what is true about this reaction ?
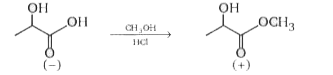
Esterification (shown below) is a reaction converting a carboxylic acid toits ester. Itinvolves only the carbonyl carbon. Esterification of (-) -lactic acid with methanol yields (+)-methyl lactate. Assuming that there are no side reactions, what is true about this reaction ?
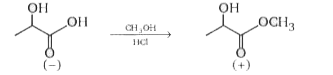
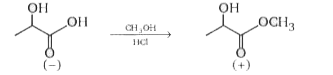
A
`AnS_(N^2)` process has occurred, inverting the absolute configuration of the chiral center
B
`AnS_(N^1)` reaction at the chiral center has inverted the optical rotation
C
A diastereomer has been produced, diastereomers have different physical properties including optical rotation
D
Optical rotation is notdirectly related to absolute configuration, so the change in sign of rotation is merely a coincidence
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Chiral center is not affected during the reaction so change in sign ofrotation is merely a coincidence.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution has been studied by titrating the liberated acetic acid against sodium hydroxide. The concentration of the ester at different times is given below. Show that it follows a pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains nearly constant (55 mol L^(-1)), during the course of the reaction. What is the value of k in this equation? Rate =k'[CH_(3) COOCH_(3) ][H_(2)O]
Amines are less reactive in substitution reactions. Their reactivity is much lesser than alcohols and alkylflourides towards substitution. Protonation of the amino group makes it a better leaving group, but not nearly as good a leaving group as a protonated alcohol. Protonated amino groups cannot be displaced by OH^(-) because it would react immediately with the acidic hydrogen which would convert it in to a poor nucleophile. The leaving group in quartenary ammonium ion has about the same leaving tendency as a protonated amino group but does not have acidic hydrogen. The reaction of a quartenary ammonium ion with hydroxide ion is known as Hoffmann elimination reaction. The leaving group is tertiary amine. Since a tertiary amine is only a moderately good leaving group, the reaction requires heat. The carbon to which the tertiary amine is attached is designated as alpha carbon. When the hydroxide ion starts to remove a beta H from a quartenary ammonium ion, the leaving group does not immediately start to leave because a tertiary amine is not a good leaving group. As a result, a partial negative charge builds up on the carbon from which the proton is removed. Which of the following statements are true regarding Hoffmann elimination ?
Amines are less reactive in substitution reactions. Their reactivity is much lesser than alcohols and alkylflourides towards substitution. Protonation of the amino group makes it a better leaving group, but not nearly as good a leaving group as a protonated alcohol. Protonated amino groups cannot be displaced by OH^(-) because it would react immediately with the acidic hydrogen which would convert it in to a poor nucleophile. The leaving group in quartenary ammonium ion has about the same leaving tendency as a protonated amino group but does not have acidic hydrogen. The reaction of a quartenary ammonium ion with hydroxide ion is known as Hoffmann elimination reaction. The leaving group is tertiary amine. Since a tertiary amine is only a moderately good leaving group, the reaction requires heat. The carbon to which the tertiary amine is attached is designated as alpha carbon. When the hydroxide ion starts to remove a beta H from a quartenary ammonium ion, the leaving group does not immediately start to leave because a tertiary amine is not a good leaving group. As a result, a partial negative charge builds up on the carbon from which the proton is removed. The compounds 'C' in question number 31 on heating with moist silver oxide gives
Amines are less reactive in substitution reactions. Their reactivity is much lesser than alcohols and alkylflourides towards substitution. Protonation of the amino group makes it a better leaving group, but not nearly as good a leaving group as a protonated alcohol. Protonated amino groups cannot be displaced by OH^(-) because it would react immediately with the acidic hydrogen which would convert it in to a poor nucleophile. The leaving group in quartenary ammonium ion has about the same leaving tendency as a protonated amino group but does not have acidic hydrogen. The reaction of a quartenary ammonium ion with hydroxide ion is known as Hoffmann elimination reaction. The leaving group is tertiary amine. Since a tertiary amine is only a moderately good leaving group, the reaction requires heat. The carbon to which the tertiary amine is attached is designated as alpha carbon. When the hydroxide ion starts to remove a beta H from a quartenary ammonium ion, the leaving group does not immediately start to leave because a tertiary amine is not a good leaving group. As a result, a partial negative charge builds up on the carbon from which the proton is removed. Which of the following statements is correct?
1) The -=C-H unit of an alkyne is more acidic than a C – H unit of an alkene or alkane, allowing acetylene and terminal alkynes to be converted to their conjugate bases -= C . 2) Unlike alkenes, alkynes are reduced by metals, especially Li, Na and K. 3) Unlike alkenes, alkynes can undergo nucleophilic as well as electrophilic addition. Which of the following best describes what happens in the first step in the mechanism of the hydrogen - deuterium exchange reaction shown? CH_3 -= CD underset(NH_3)overset(NaNH_2)to CH_3C -= CH
1) The -=C-H unit of an alkyne is more acidic than a C – H unit of an alkene or alkane, allowing acetylene and terminal alkynes to be converted to their conjugate bases -= C . 2) Unlike alkenes, alkynes are reduced by metals, especially Li, Na and K. 3) Unlike alkenes, alkynes can undergo nucleophilic as well as electrophilic addition. Which of the following best describes what happens in the first step in the mechanism of the reaction shown? CH_3 CH_2CH_2CHBr_2 + 3NaNH_2 overset(NH_3)to CH_3CH_2C -=CNa +2NaBr +3NH_3