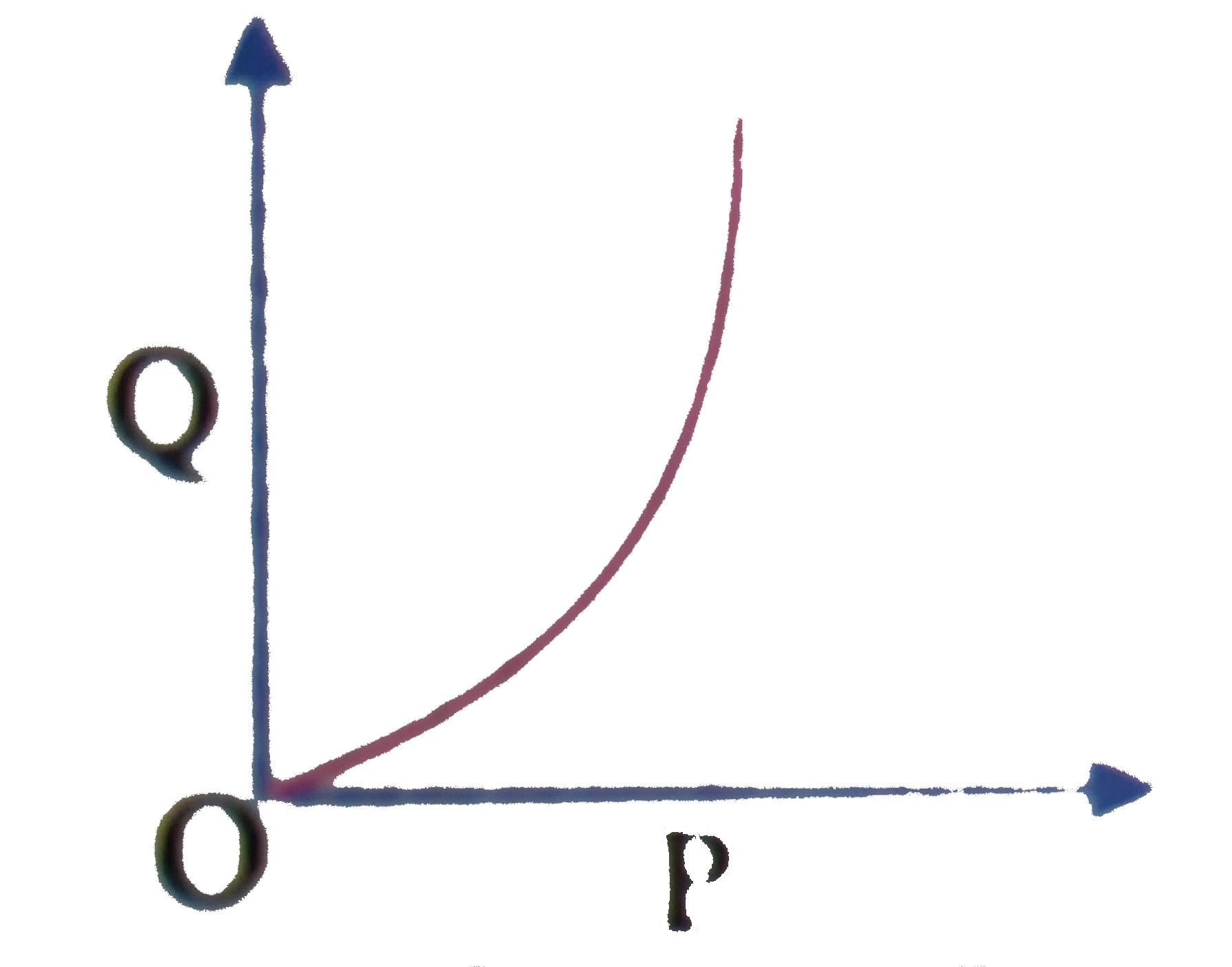
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELASTICITY
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Bulk Modulus)|11 VideosELASTICITY
ERRORLESS|Exercise NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Modulus of Rigidity)|16 VideosELASTICITY
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON |10 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS AND VECTORS
ERRORLESS|Exercise Assertion & Reason|15 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
ERRORLESS|Exercise ASSERTION AND REASON|23 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS-ELASTICITY-NCERT BASED QUESTIONS (Work Done in Stretching a Wire)
- A metallic rod of length l and cross-sectional area A is made of a mat...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the work done, if a wire is loaded by 'Mg' weight and the in...
Text Solution
|
- An elastic material of Young's modulus Y is subjected to a stress S. ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length L and cross sectional area A is made of a material of...
Text Solution
|
- Young's modulus of the material of a wire is Y. ON pulling the wire by...
Text Solution
|
- The work per unit volume to stretch the length by 1% of a wire with cr...
Text Solution
|
- When a force is applied on a wire of uniform cross-sectional are 3 xx ...
Text Solution
|
- K is the force constant of a spring. The work done in increasing its e...
Text Solution
|
- A metal rod of length 'L', cross-sectional area 'A', Young's modulus '...
Text Solution
|
- Two, spring P and (Q) of force constants K(p) and k(Q)(k(Q)=(kp)/2)are...
Text Solution
|
- The length of a wire is 1.0 m and the area of cross-section is 1.0 xx ...
Text Solution
|
- A rubber cord catapult has cross-sectional area 25 mm^(2) and initial ...
Text Solution
|
- The graph show the behaviour of a length of wire in the region for whi...
Text Solution
|