Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HYDROCARBONS
PRADEEP|Exercise ADVANCED PROBLEMS FOR COMPETITION|5 VideosHYDROCARBONS
PRADEEP|Exercise PROBLEMS FOR PRACTICE|3 VideosHYDROCARBONS
PRADEEP|Exercise Competition Focus (JEE(main and advanced)/Medical Entrance) VIII. ASSERTION - REASON TYPE QUESTIONS|31 VideosEQUILIBRIUM IN PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES
PRADEEP|Exercise Competition Focus (Jee(Main and advanced)/Medical Entrance) VIII. ASSERTION - REASON TYPE QUESTIONS (TYPE - II)|10 VideosHYDROGEN
PRADEEP|Exercise COMPETITION FOCUS (Assertion-Reason Type Questions) Type 2|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-HYDROCARBONS-CURIOSITY QUESTIONS
- Acetylene is said to be acidic ? Does it mean that it turns blue litmu...
Text Solution
|
- Does acetylene react with Fehling's solution ?
Text Solution
|
- What would have been the shape of benzene molecule had there been no r...
Text Solution
|
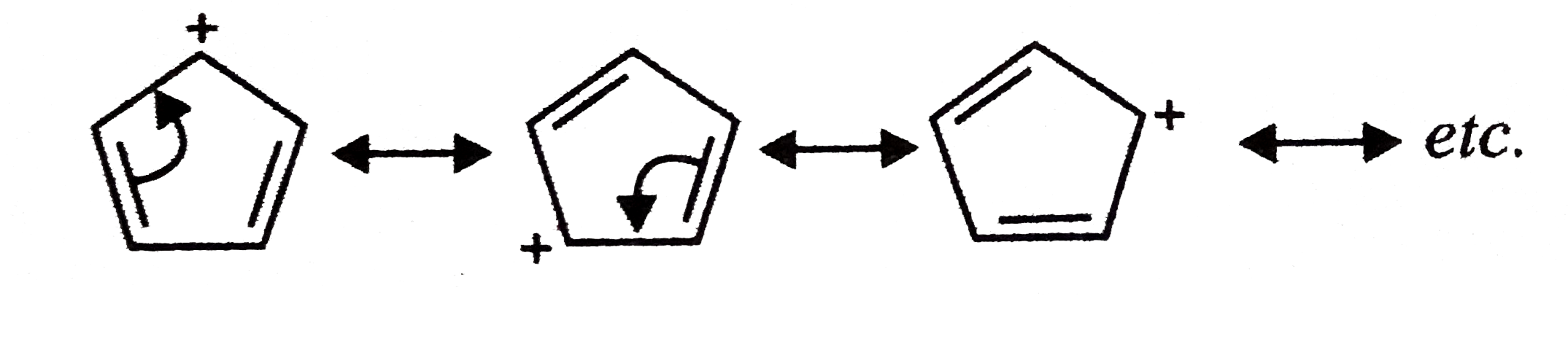
- Does resonance always lead to stabilization of cyclic conjugated syste...
Text Solution
|