Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise SECTION-J AAKASH CHALLENGERS QUESTIONS|10 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment(Section-D)(Assertion - Reason Type Questions)|12 VideosPOLYMERS
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION-D)|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES-TRY YOURSELF
- Indicate the sigma & pi bonds in (i) CH(2)Cl(2) (ii) CH(3)-C-=C-CH...
Text Solution
|
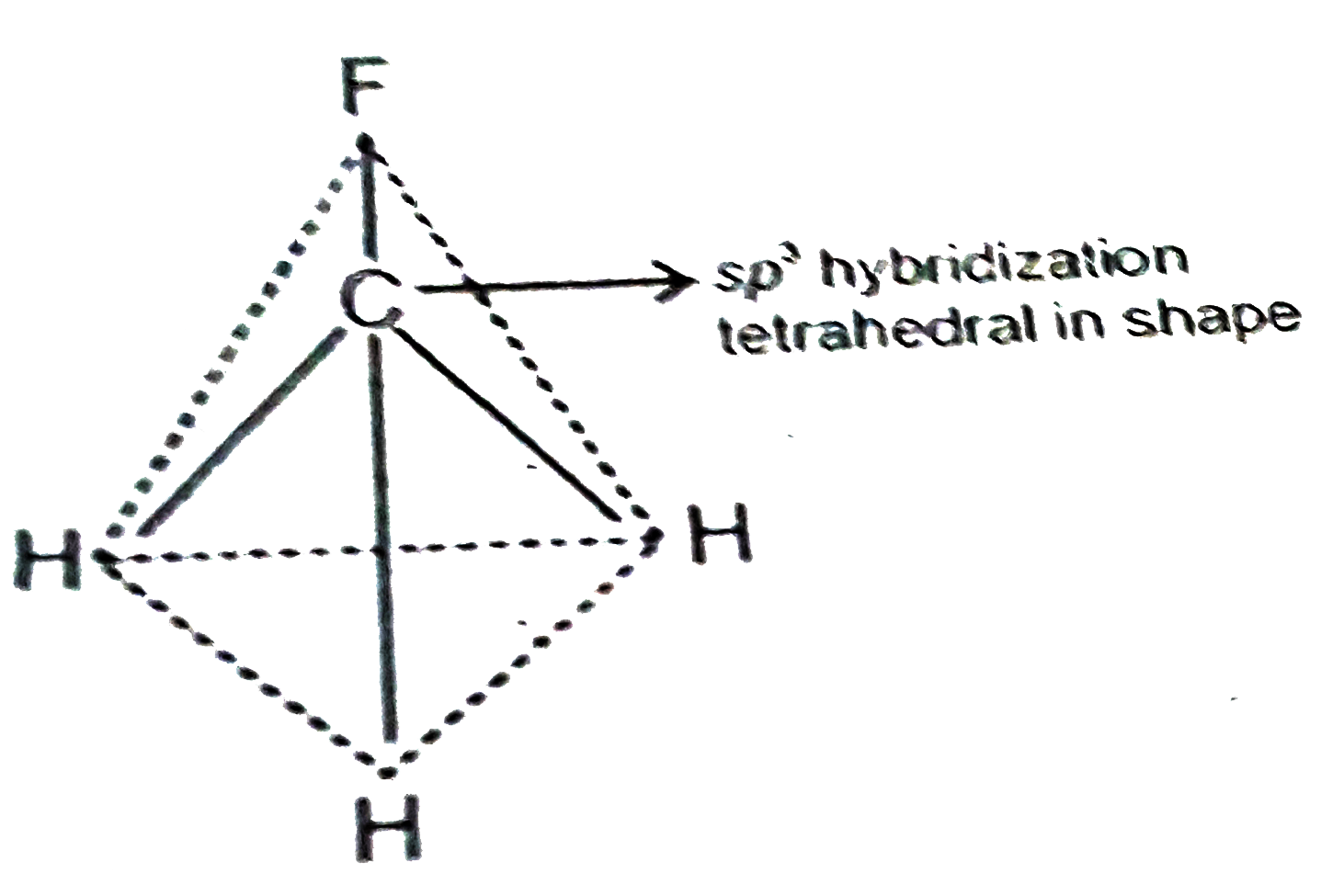
- On the basis of hydribidsation predict the shape of the following mole...
Text Solution
|
- Write its bond line formula (i) CH(3)CH(OH)CH(2)CH(2)OH
Text Solution
|
- Expand each of the structure
Text Solution
|
- Draw the bond line structure for
Text Solution
|
- Write three-dimensional representation for CH(3)CH(2)OH compound.
Text Solution
|
- Give the IUPAC name
Text Solution
|
- Give its IUPAC name.
Text Solution
|
- Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds (i) CH(3)-CH(2)-ove...
Text Solution
|
- Derive the structure of (i) 2-Chlorohexane, (ii) Pent-4-en-2-ol, (iii)...
Text Solution
|
- Draw all the possible isomers of C(4)H(8)O (containing carbony group)
Text Solution
|
- What is the relation between 2-methyl propanaol-1 and 2-methoxy propan...
Text Solution
|
- Using the curved-arrow notation, show the formation of reactive interm...
Text Solution
|
- Classify the following molecules/ions as nucleophiles or electrophiles...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonating strcuture for C(6)H(5)CHO compound.
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following carbocations in increasing order of stability an...
Text Solution
|
- On complete combustion, 0.246 g of an organic compound gave 0.198g of ...
Text Solution
|
- 0.2613g of an organic compound on combustion in oxygen gave 0.8844 g o...
Text Solution
|
- 0.2313 g of an organic substance gave 40 ml of moist nitrogen measured...
Text Solution
|
- 0.27g of an organic compound gave on combustion 0.396 of CO(2) 0.216g ...
Text Solution
|