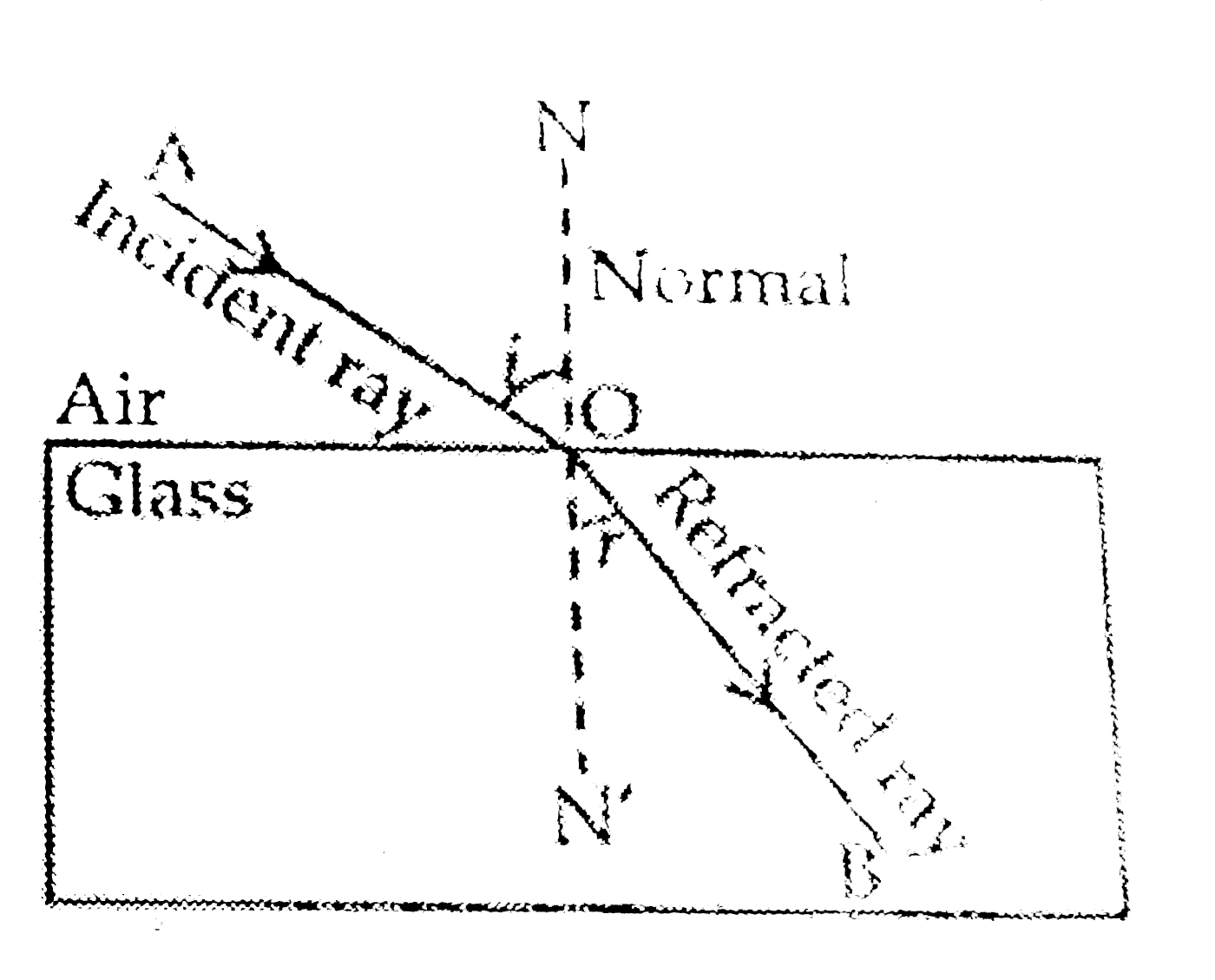
(a) There are two laws of refractions of light .
(i) The first law of refraction of light states that the incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The second law of refraction of light is the Snell's law of Refraction. It states that the ratio of sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refractions is a constant for a given pair of medium.
`(sini)/(sinr)="constant"(n)`
This constant (n) is called refractive index of the medium.
Absolute refractive index of a medium `=("Speed of light in vacuum")/("Speed of light in medium")`
(b) `""_(a)n_(w) =(4)/(3) " "_(a)n_(g)=(3)/(2)`
Speed of light in glass , `v_(g)=2xx10^(8) m//s`
Speed of light in air, `v_(a) =? " Speed of light in water , "v_(w)=?`
`""_(a)n_(w) =(v_(a))/(v_(w)) rArr (4)/(3)=(v_(a))/(v_(w)) " " ` ...(i)
`""_(a)n_(g) =(v_(a))/(v_(g)) rArr (3)/(2) = (v_(a))/(2xx10^(8))`
`rArr v_(a) =(3)/(cancel(2))xxcancel(2) xx 10^(8) m//s`
Putting the value of `v_(a)` in equation (i),
`(4)/(3) =(3xx10^(8))/(v_(w)) rArr v_(w)=3xx10^(8)xx(3)/(4)=(9)/(4)xx10^(8) `
`=2.25 xx 10^(8) m//s`