Ohm's law states that the electric current, through a conductor, is directly proportional to the potential difference across its two ends when, other physical condition like temperature, etc., remain constant.
`V prop I`
`or (V)/(I) = "Constant" = R`
`or V = IR`
Thus, the ratio V : I is a constant. This constant is called the resistance (R) of the conductor.
Circuit diagram for Ohm's law:
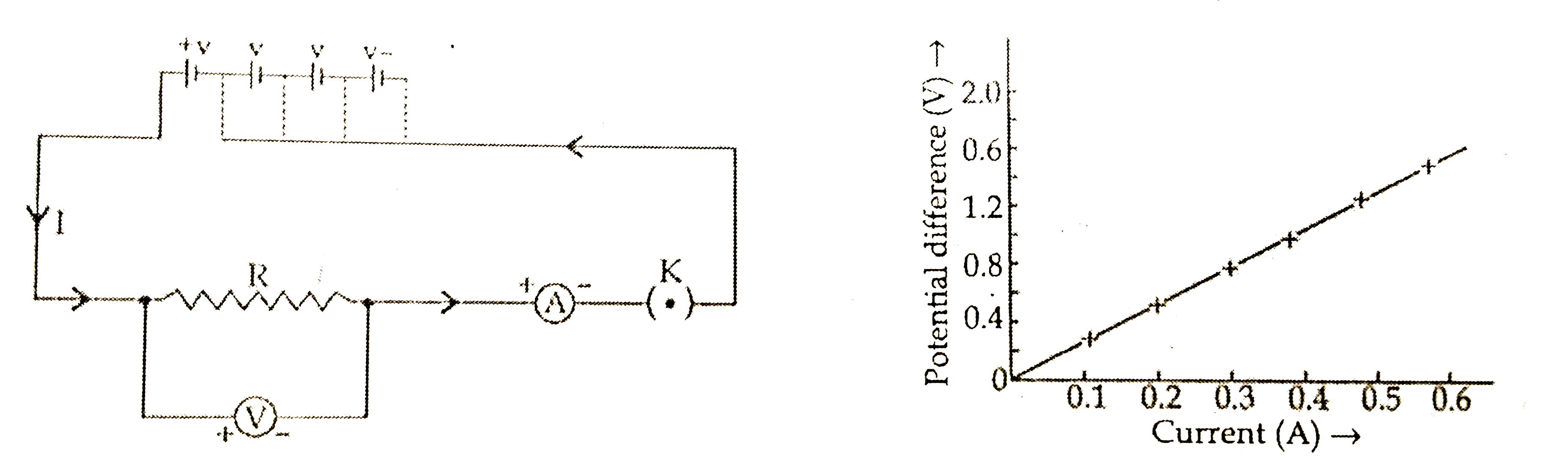
Explanation. If a graph is drawn between the potential difference (V) and current (I), the graph is found to be a straight line passing through the origin. This shows current is directly proportional to the potential difference. Thus the ratio `(V)/(I)` remains constant. This constant is called the resistance of the conductor. The gradient of the straight ling graph is related to the resistance (R) of the conductor.