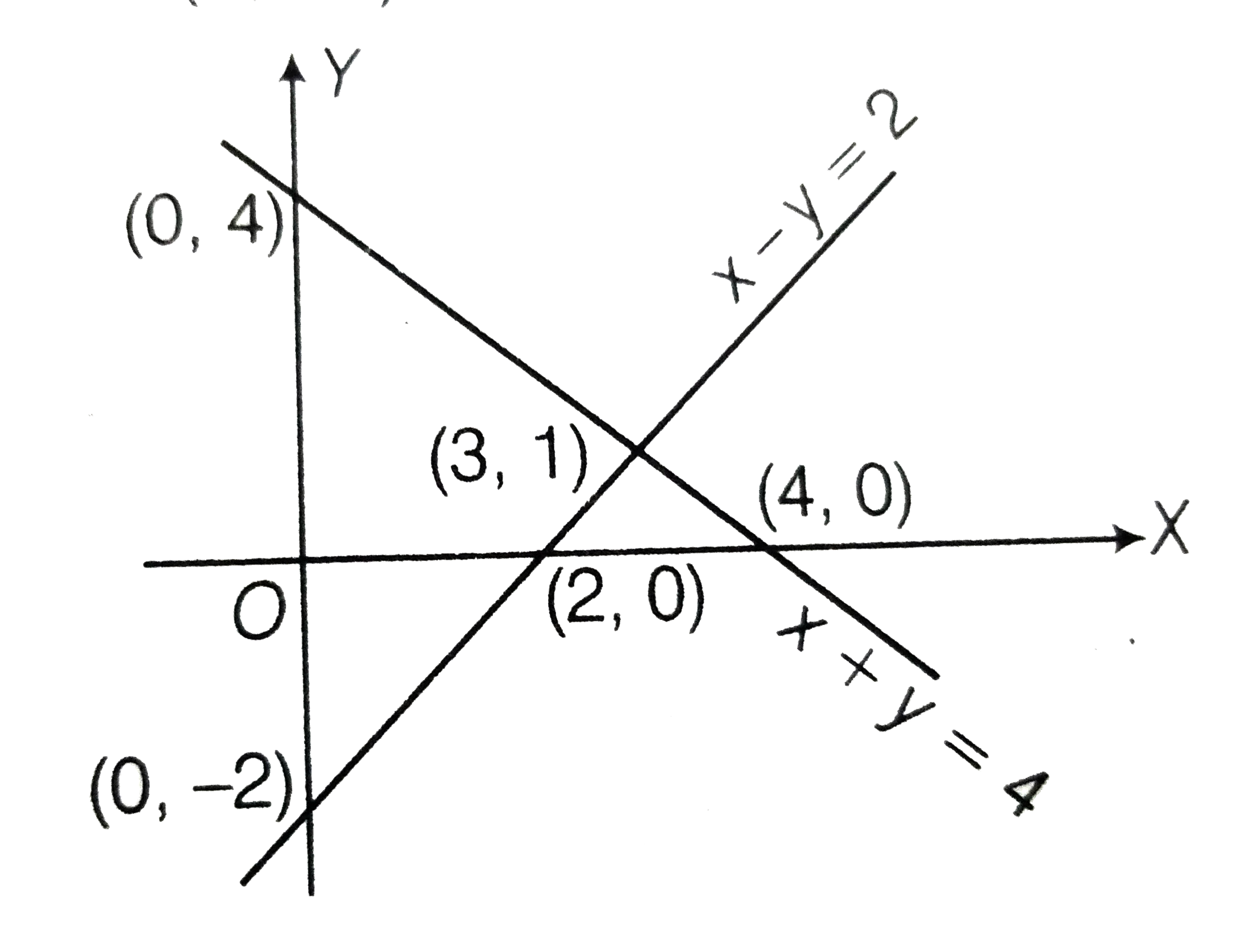
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS-PRACTICE SET 10-PAPER 2 (MATHEMATICS)
- The second order derivative of a sin^3 t w.r.t, a cos^3 t at t = pi/4...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of the plane passing through the points (1,2,3), (-1,4,2)...
Text Solution
|
- To maximise the objective function z=x+2y under the constraints x-y le...
Text Solution
|
- If (sin(x+y))/(sin(x-y))=(a+b)/(a-b) , then show that (tanx)/(tany)=(...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation lamdax^(2)+(2lamda-3)y^(2)-4x-1=0 represents a circle,...
Text Solution
|
- If the lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of the ...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between the foci of the conic 7x^(2)-9y^(2)=63 is equal t...
Text Solution
|
- The line l x+m y+n=0 is a normal to the ellipse (x^2)/(a^2)+(y^2)/(...
Text Solution
|
- The angle of intersection of the curves y=x^(2)andx=y^(2) at (1,1) is
Text Solution
|
- A straight line passing through the point(2,2) and the axes enclose an...
Text Solution
|
- If a committee of 3 is to be chosen from a group of 38 people of which...
Text Solution
|
- The real number x when added to its inverse given the minimum value of...
Text Solution
|
- The value of underset(xto2)(e^(3x-6)-1)/(sin(2-x))
Text Solution
|
- If f(x)=3x^(4)+4x^(3)-12x^(2)+12, then f(x) is
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following functions, Rolle's theorem is applicable?
Text Solution
|
- An edge of a variable cube is increasing at the rate of 10cm/sec. How ...
Text Solution
|
- The general solution of y^(2)dx+(x^(2)-xy+y^(2))dy=0, is
Text Solution
|
- cos{cos^(-1)(-1/7)+sin^(-12)(-1/7)} =
Text Solution
|
- In any triangle ABC, if a=\ 18 , b=\ 24 , c=\ 30, findsinA, sinB, sinC
Text Solution
|
- (d)/(dx)(logx)^(4) is equal to
Text Solution
|