Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-HEAT TRANSFER-Exercises
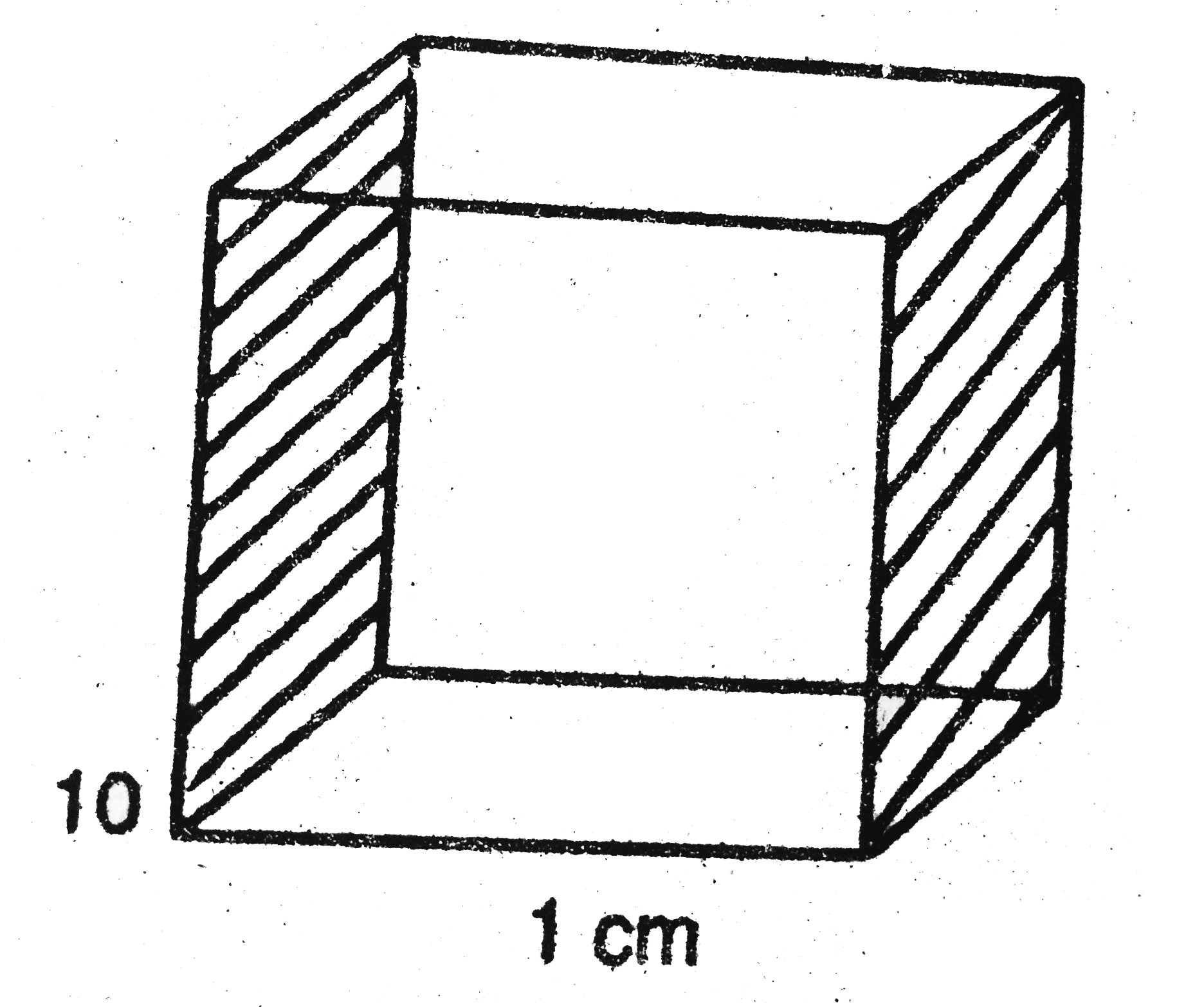
- A uniform slab of dimension 10cmxx10cmxx1cm is kept between two heat r...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid-nitrogen container is made of a 1-cm thick styrofoam sheet ha...
Text Solution
|
- The normal body-temperature of a person is 97(@)F . Calculate the rate...
Text Solution
|
- Water is boiled in a container having a bottom of surface area 25cm^(2...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a steel rod (K=46Js^(-1)m^(-1)^(@)C^(-1) of length 1.0m is ...
Text Solution
|
- An icebox almost comletely filled with ice at 0^(@)C is dipped into a ...
Text Solution
|
- A pitcher with 1-mm thick porous walls contain 10kg of water. ,Water c...
Text Solution
|
- A steel farme (K=45Wm^(-1)^(@)C^(-1) of total length 60cm and cross se...
Text Solution
|
- Water at 506(@)C is filled in a closed cylindercal vessel of height 10...
Text Solution
|
- The lleft end of a copper rod (length=20cm. Area of cross section=0.02...
Text Solution
|
- The ends of a metre stick are maintain at 100^(@)C and 0^(@)C . One en...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical box of volume 216cm^(3) is made up of 0.1cm thick wood, The ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows water in a container having 2.0-mm thick walls made of a ...
Text Solution
|
- On a winter day when the atmospheric temperature drops to -10^(@)C , i...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation of the previous problem. Assume that the temper...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of lengths 20cm eac h and area of cross section 1cm^(2) are...
Text Solution
|
- A semicircular rods is joined at its end to a straight rod of the same...
Text Solution
|
- A metal rod of cross sectional area 1.0cm^(2) is being heated at one e...
Text Solution
|
- Steam at 120^(@)C is continuously passed through a 50-cm long rubber t...
Text Solution
|
- A hole of radius r(1) is made centrally in a uniform circular disc of ...
Text Solution
|