Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-HEAT TRANSFER-Exercises
- A hollow tube has a length l, inner radius R(1) and outer radius R(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- A composite slab is prepared by pasting two plates of thickness L(1) a...
Text Solution
|
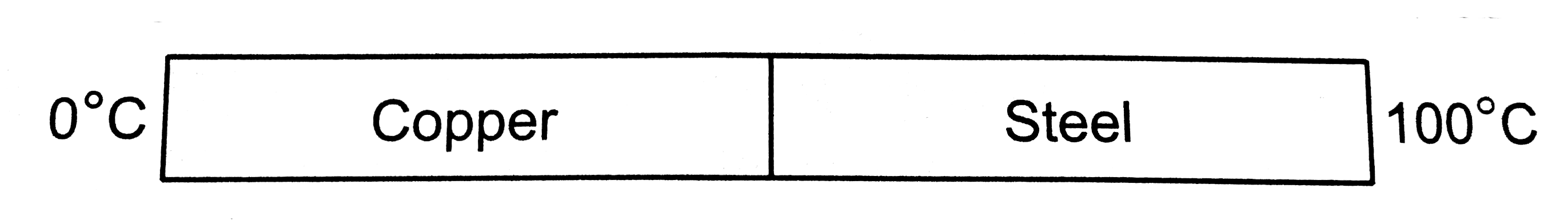
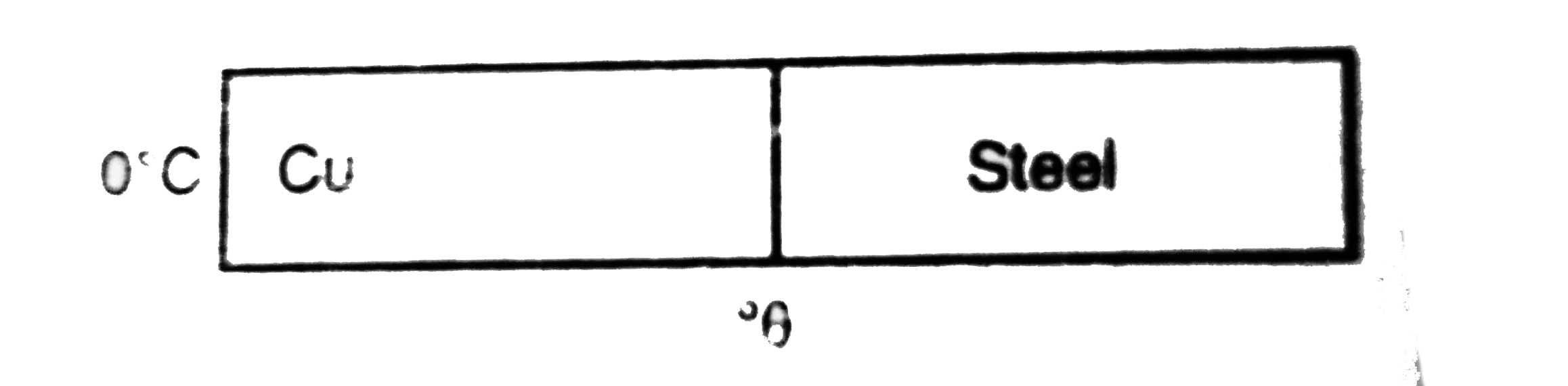
- Figure shows a copper rod joined to a steel rod. The rods have equal l...
Text Solution
|
- An aluminium rod and a copper rod of equal length 1.0 m and cross-sect...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an aluminium rod joined to a copper rod. Each of the rods...
Text Solution
|
- Conside the situation shown in figure. The frame is made of the same m...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the bent part of the frame of the previous problem has a therm...
Text Solution
|
- A room has s window fitted with a single 0.1mxx2.0m glass of thickness...
Text Solution
|
- The two rods show in figure have identical geomerical dimension.. They...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical rods AB, CD, CF and DE are joined as shown in figure. T...
Text Solution
|
- Seven rods A, B, C, D, E, F and G are joined as shown in figure. All t...
Text Solution
|
- Find the rate of heat flow through a cross section of the rod shown in...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of negligible heat capacity has length 20cm, area of cross secti...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow metallic sphere of radius 20cm surrounds a concentric metalli...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown two adiabatic vessels, each containing a mass m of water ...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of masses m(1) and m(2) and specific heat capacities S(1) a...
Text Solution
|
- An amount n (in moles) of a monatomic gas at initial temperature T(0) ...
Text Solution
|
- Assume that the total surface area of a human body is 1-6m^(2) and tha...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the amount of heat radiated per second by a body of surface ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid aluminium sphere and a solid copper sphere of twice the radius...
Text Solution
|