Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUNIL BATRA (41 YEARS IITJEE PHYSICS)-HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICS-JEE Main And Advanced
- A solid copper sphere (density rho and specific heat c) of radius r at...
Text Solution
|
- A point source of heat of power P is placed at the centre of a spheric...
Text Solution
|
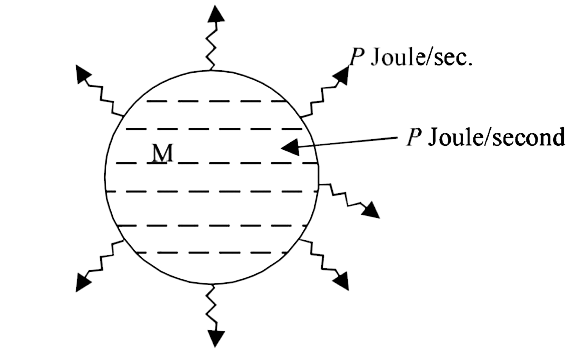
- A substance of mass M kg requires a power input of P wants to remain i...
Text Solution
|
- A container of volume 1m^3 is divided into two equal parts by a partit...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas with pressure P, volume V and temperature T is expanded i...
Text Solution
|
- Two metal cubes A and B of same size are arranged as shown in Figure. ...
Text Solution
|
- A ring shaped tube contain two ideal gases with equal masses and relat...
Text Solution
|
- Earth recieves 1400 W//m^2 of solar power. If all the solar energy fal...
Text Solution
|
- The root-mean square speeds of the molecules of different ideal gses, ...
Text Solution
|
- The volume V versus temperature T graphs for a cetain amount of a perf...
Text Solution
|
- Two different gases at the same temperature have equal root mean squar...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of the velocity of sound in Hydrogen gas (gamma=7/5) to that...
Text Solution
|
- The curves A and B in the figure shown P-V graphs for an isothermal an...
Text Solution
|
- At a given temperature, the specific heat of a gas at constant pressur...
Text Solution
|
- The root mean square (rms) speed of oxygen molecules (O2) at a certa...
Text Solution
|
- Two spheres of the same material have radii 1m and 4m and temperatures...
Text Solution
|
- A constant volume gas thermometer works on
Text Solution
|
- A metal ball immersed in alcohol weights W1 at 0^@C and W2 at 50^@C. T...
Text Solution
|
- A wall has two layers A and B, each made of different material. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monatomic gas is taken round the cycle ABCDA as shown in the ...
Text Solution
|