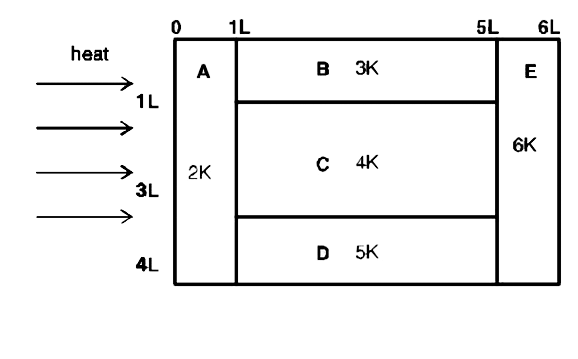
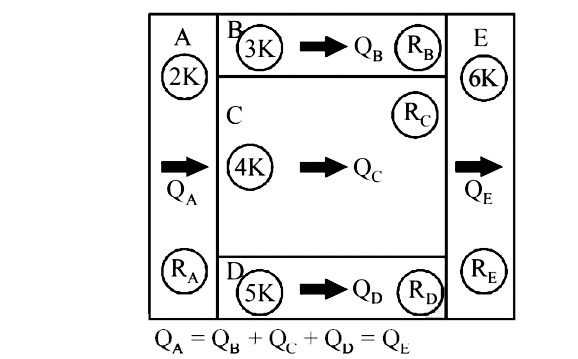
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUNIL BATRA (41 YEARS IITJEE PHYSICS)-HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICS-JEE Main And Advanced
- The figure shows the P-V plot of an ideal gas taken through a cycle AB...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas in initial state A undergoes a cylic process ...
Text Solution
|
- A composite block is made of slabs A,B,C,D and E of different thermal ...
Text Solution
|
- The figure below shows the variation of specific heat capacity (C) of ...
Text Solution
|
- A container of fixed volume has a mixture of a one mole of hydrogen an...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a horizontal cylinder by a spri...
Text Solution
|
- A sinker of weight w0 has an apparent weight w1 when weighed in a liqu...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of material X and three rods of material Y are connected as...
Text Solution
|
- Given samples of 1 c.c. of hydrogen and 1 c.c. of oxygen, both at N.T....
Text Solution
|
- A solid material is supplied with heat at a constant rate. The tempera...
Text Solution
|
- A jar contains a gas and a few drops of water at absolute temperture T...
Text Solution
|
- A cyclic process ABCA shown in the V-T diagram is performed with a con...
Text Solution
|
- A lead bullet just melts when stopped by an obstacle. Assuming that 25...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the work done when one mole of a perfect gas is compressed a...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of copper of radius R and a hollow sphere of the same m...
Text Solution
|
- 1 g mole of oxygen at 27^@ C and 1 atmosphere pressure is enclosed in...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangualr box (shown in figure) has a movable and smooth portition...
Text Solution
|
- Two glass bulbs of equal volume are connected by a narrow tube and are...
Text Solution
|
- A thin tube of uniform cross section is sealed at both ends. It lies h...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas has a specific heat at constant pressure CP=(5R)/2. The g...
Text Solution
|