Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-GRAVITATION-(C) Chapter Exercises
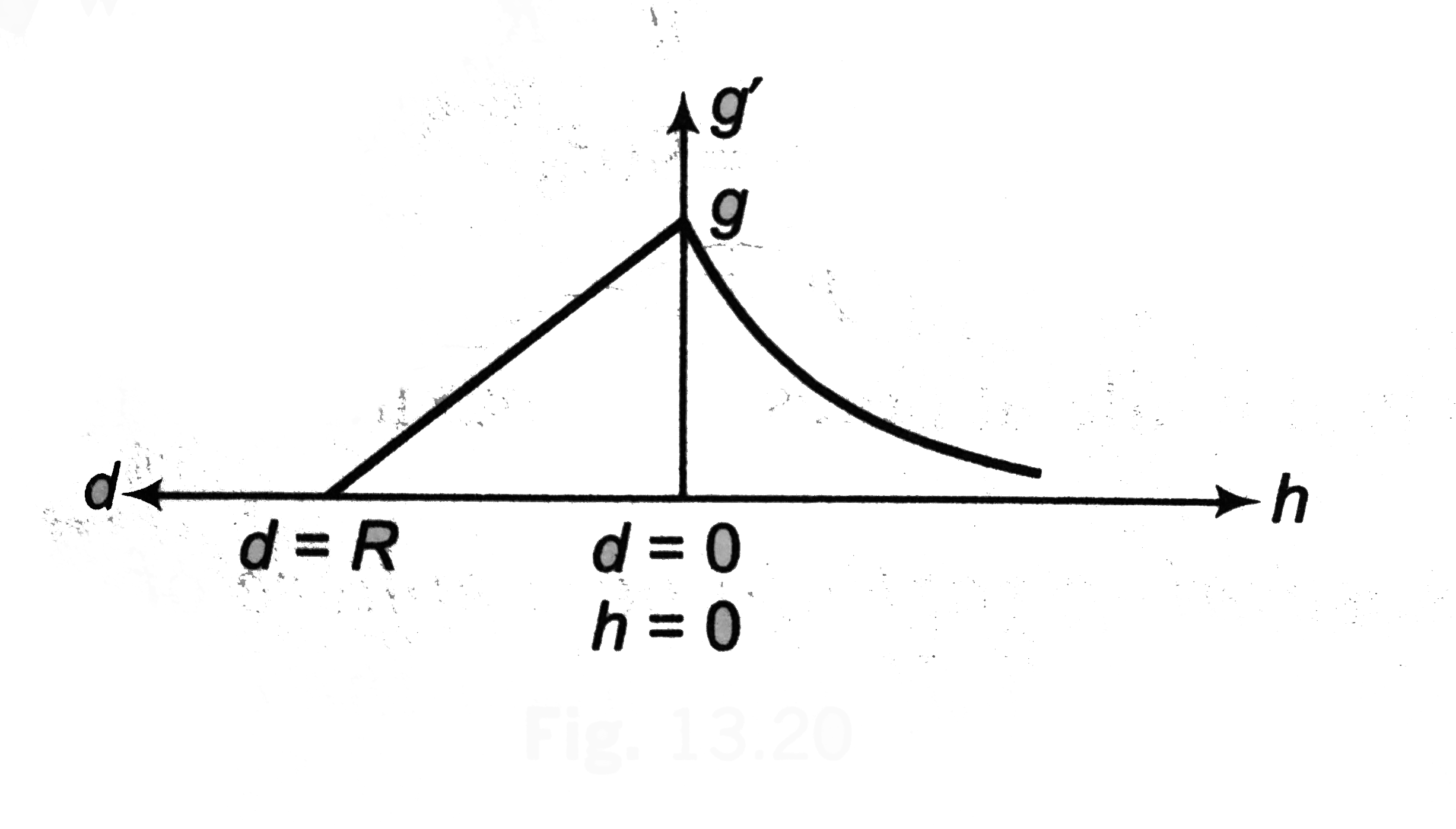
- Draw g' versus d and g' versus h graph. Here, 'd' is depth below the s...
Text Solution
|
- Starting from the centre of the earth having radius R, the variation o...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite of mass m is orbiting the earth (of radius R) at a height ...
Text Solution
|
- At what height from the surface of earth the gravitation potential and...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of escape velocity at earth (v(e)) to the escape velocity at...
Text Solution
|
- Kepler's third law states that square of period revolution (T) of a pl...
Text Solution
|
- The reading of a spring balance corresponds to 100 N while situated at...
Text Solution
|
- The gravitational field due to an uniform solid sphere of mass M and r...
Text Solution
|
- What would be the value of acceleration due to gravity at a point 5 km...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of equal mass (m) each move in a circle of radius (r) un...
Text Solution
|
- What would be the escape velocity from the moon, it the mass of the mo...
Text Solution
|
- Two spheres of masses 16 kg and 4 kg are separated by a distance 30 m ...
Text Solution
|
- Orbital velocity of an artificial satellite does not depend upon
Text Solution
|
- Gravitational potential energy of body of mass m at a height of h abov...
Text Solution
|
- According to Kepler's law of planetary motion, if T represents time pe...
Text Solution
|
- If mass of a body is M on the earth surface, then the mass of the same...
Text Solution
|
- Two spherical bodies of masses m and 5m and radii R and 2R respectivel...
Text Solution
|
- The force of gravitation is
Text Solution
|
- Dependence of intensity of gravitational field (E) of earth with dista...
Text Solution
|
- Keeping the mass of the earth as constant, if its radius is reduced to...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is raised to a height 10 R from the surface of the ea...
Text Solution
|