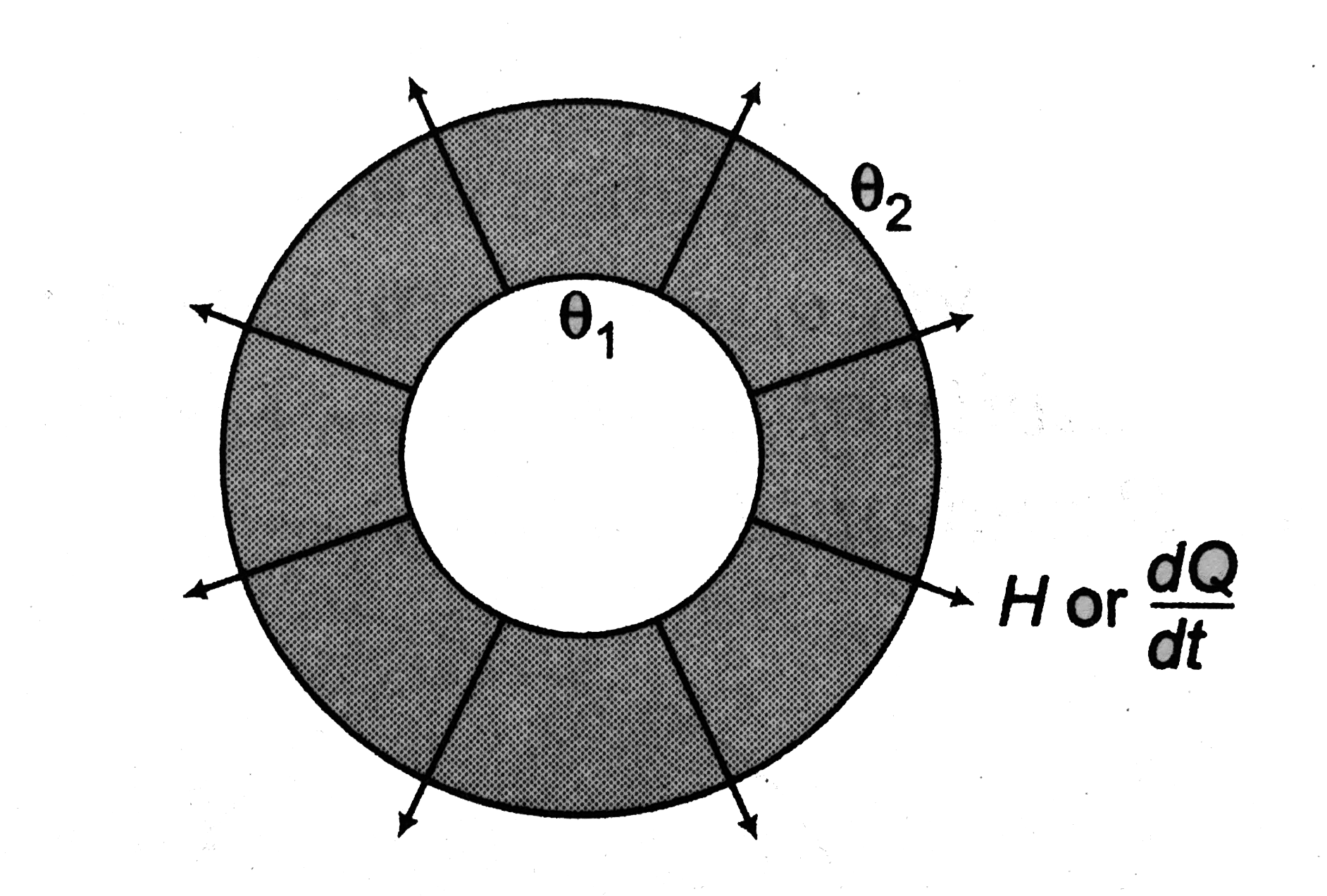
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CALORIMETRY & HEAT TRANSFER
DC PANDEY|Exercise Example Type 2|2 VideosCALORIMETRY & HEAT TRANSFER
DC PANDEY|Exercise Example Type 3|1 VideosCALORIMETRY & HEAT TRANSFER
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 Subjective|14 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise|13 VideosCALORIMETRY AND HEAT TRANSFER
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrance s gallery|38 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CALORIMETRY & HEAT TRANSFER-Example Type 1
- Thermal conductivity of the conductor shown in figure is K. Find therm...
Text Solution
|
- Thermal conductivity of inner core of radius r is K and of the outer o...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical body of radius 'b' has a concentric cavity of radius 'a' a...
Text Solution
|
- In the above example, if temperature of inner surface P is kept consta...
Text Solution
|