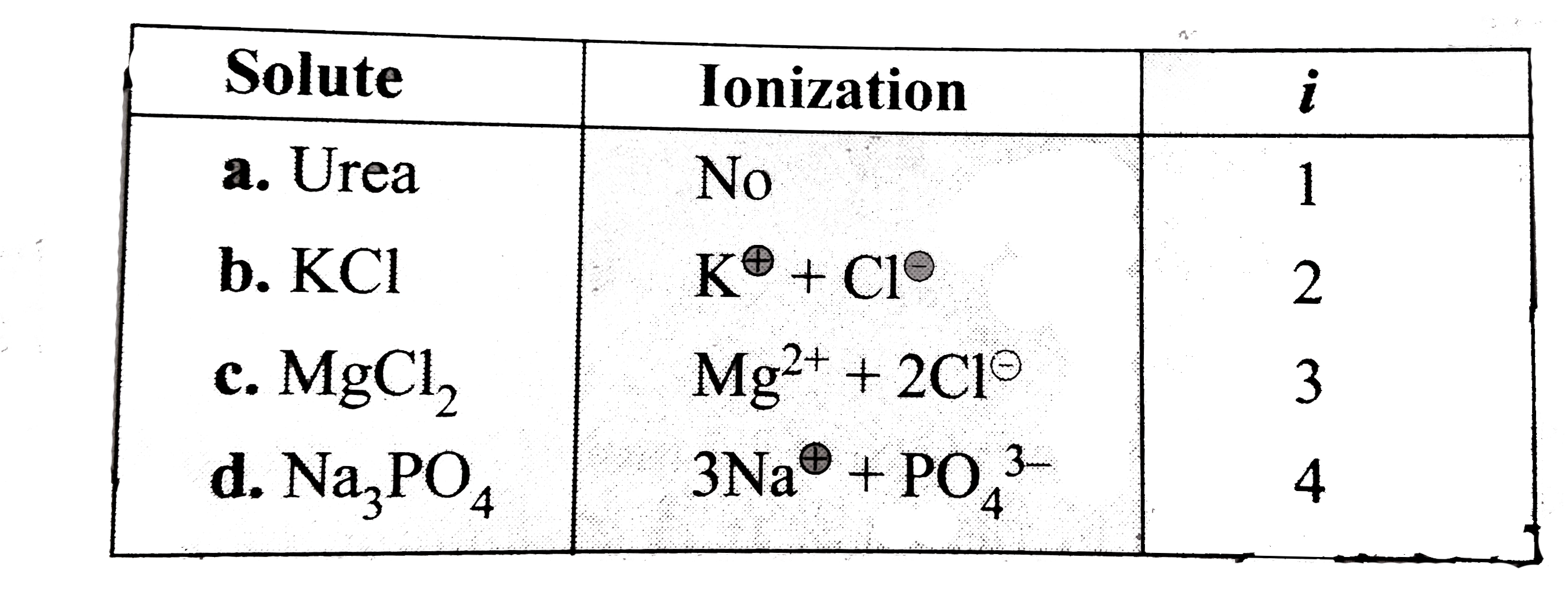Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-SOLUTIONS-Ex 2.3 (Objective)
- Follwing are equimolal aqueous solution: a.1 m urea , b.1 m KCl , c....
Text Solution
|
- What should be the boiling point of 1.0 molal aqueous KCl solution (as...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of freezing point depression values of 0.01 M solutions of u...
Text Solution
|
- From a measurement of the freezing point depression of benzene, the mo...
Text Solution
|
- An aqueous solution containing an ionic salt having molality equal to ...
Text Solution
|
- The Van't Hoff factor of a 0.1 M Al(2)(SO(4))(3) solution is 4.20. The...
Text Solution
|
- The degree of dissociation alpha of a week electrolyte is where n is...
Text Solution
|
- Increasing amount of solid Hgl(2) is added to 1 L of an aqueous soluti...
Text Solution
|
- Equimolal solutions KCl and compound X in water show depression in fre...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following solutions as directed: Increasing order of boi...
Text Solution
|