Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.1|6 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.2|17 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|11 VideosPROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|2 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Interger|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1-Solved Examples
- A uniform cylinder of radius r and mass m can rotate freely about a fi...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform bar of mass m and length 2L is held at angle 30^(@) wi...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform solid sphere of mass 1 kg and radius 10 cm is kept stationar...
Text Solution
|
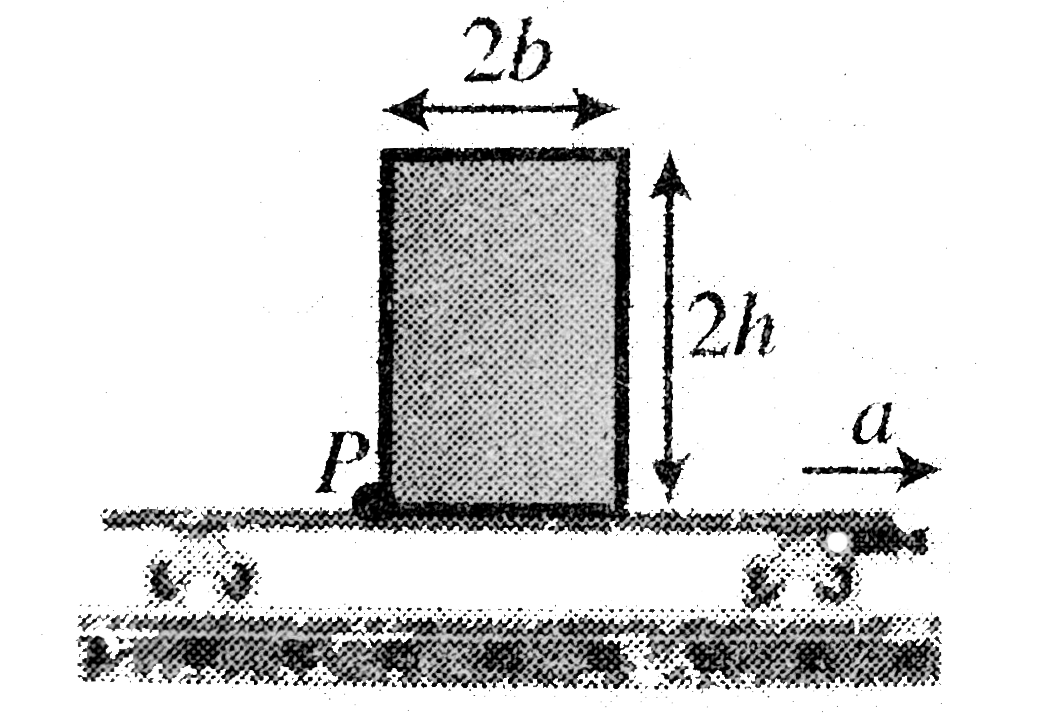
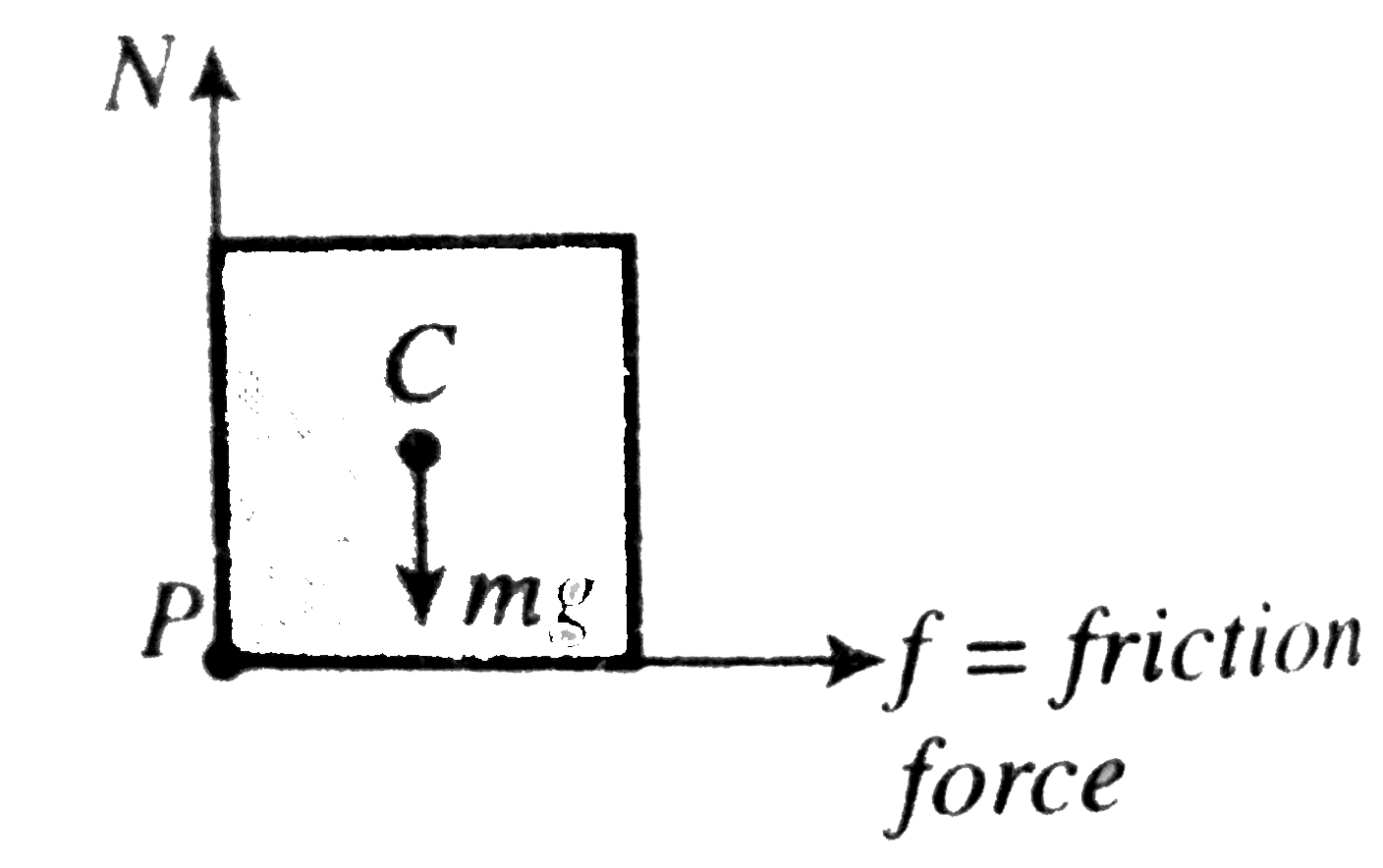
- A block of mass m height 2h and width 2b rests on a flat car which mo...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform slender bar AB of mass m is suspended as shown from a small ...
Text Solution
|
- One fourth length of a uniform rod of length 2l and mass m is place do...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the minimum coefficient of friction between a thin rod and a...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two heavy right circular rollers of the radii R and r respect...
Text Solution
|
- In the system shown in the figure blocks A and B have mass m(1)=2 kg a...
Text Solution
|