The two discs exert equal and opposite forces on each other when in contact. The torque due to these forces change the angular momentum of each disc. Form angular impulse angular momentum theorem, we have
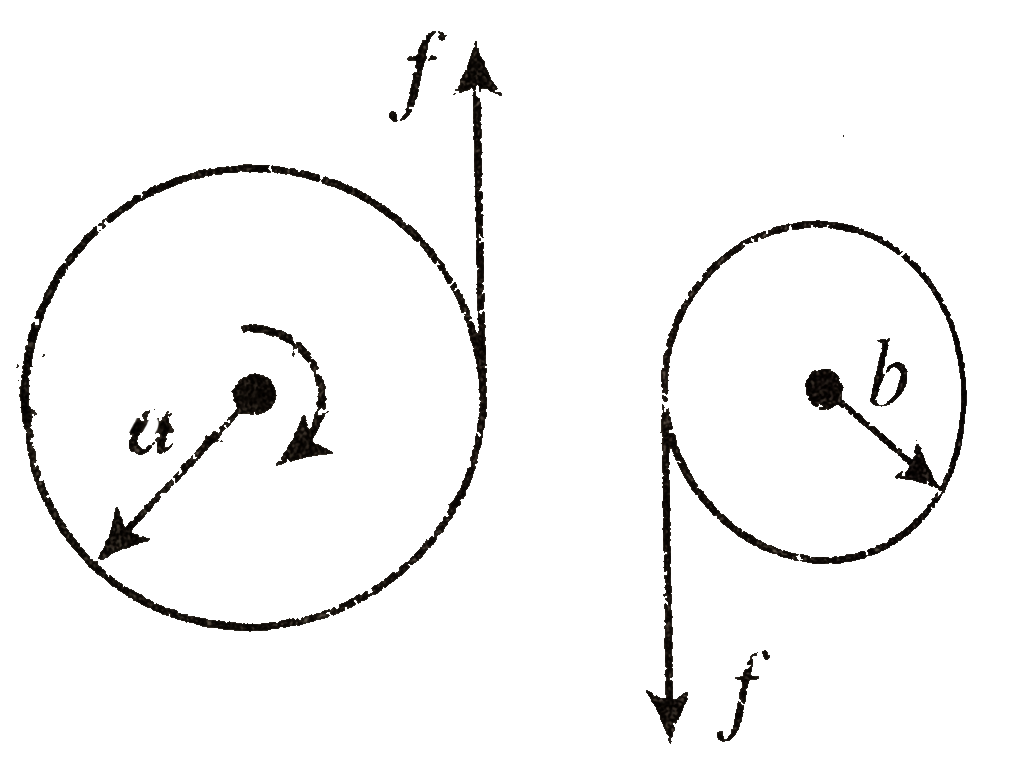
`fa/_\t=I_(1)(omega_(0)-omega_(1))`
and `fb/_\t=I_(2)omega_(2)`
From eqn i and ii we get
`a/b=(I_(1)(omega_(0)-omega_(1)))/(I_(2)omega_(2))`
When slipping ceaes between the disc, the contact points the two dics have the same linear velocity i.e.,
`aomega_(1)=bomega_(2)`
on substituting `omega_(2)` in eqn iii we get
`omega_(1)=((I_(1)omega_(0)))/([I_(1)+(a^(2)I_(2)//b^(2))])`