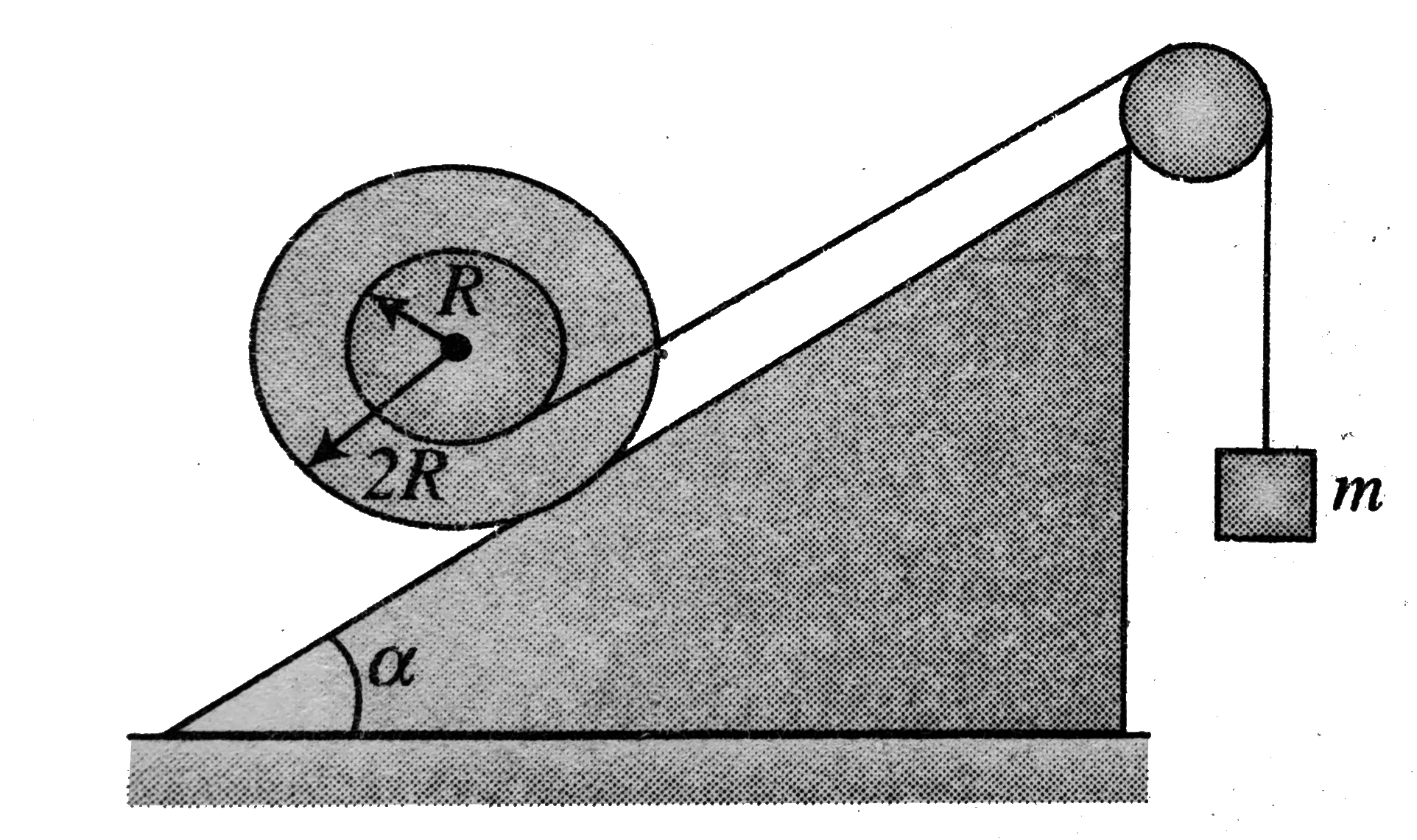
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|26 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Linked Comprehension|71 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|19 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|11 VideosSOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2-Single Correct
- A uniform rod AB of mass m length 2a is allowed to fall under gravity ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m and radius r rolls inside a hemispherical shell of ra...
Text Solution
|
- A spool of mass M and radius 2R lies on an inclined plane as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- An impulse J is applied on a ring of mass m along a line passing throu...
Text Solution
|
- If a rigid body rolls on a surface without slipping, then:
Text Solution
|
- The disc of radius r is confined to roll without slipping at A and B. ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of mass M and radius R is pulled horizontally on a roug...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is given an initial angular velocity omega(0) and placed on a r...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel is rolling on a horizontal plane. At a certain instant it has ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider three uniform solid spheres. sphere (i ) has radius r and mas...
Text Solution
|
- The uniform speed of a body is the same as seen from any point in the ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AC of length l and mass m is kept on a horizontal smooth plane. ...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal disc rotates freely about a vertical axis through its cen...
Text Solution
|
- Two horizontal discs of different radii are free to rotate about their...
Text Solution
|
- A constant external torque tau acts for a very brief period /\t on a r...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical spheres A and B are free to move and I, rotate about the...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of circumference s is at rest at a point A on a horizontal surf...
Text Solution
|
- A ring (R), a disc (D), a solid sphere (S) and a hollow sphere with th...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere rolls without slipping on a rough horizontal floor, mov...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform rod of mass m and length l is free to rotate about its ...
Text Solution
|