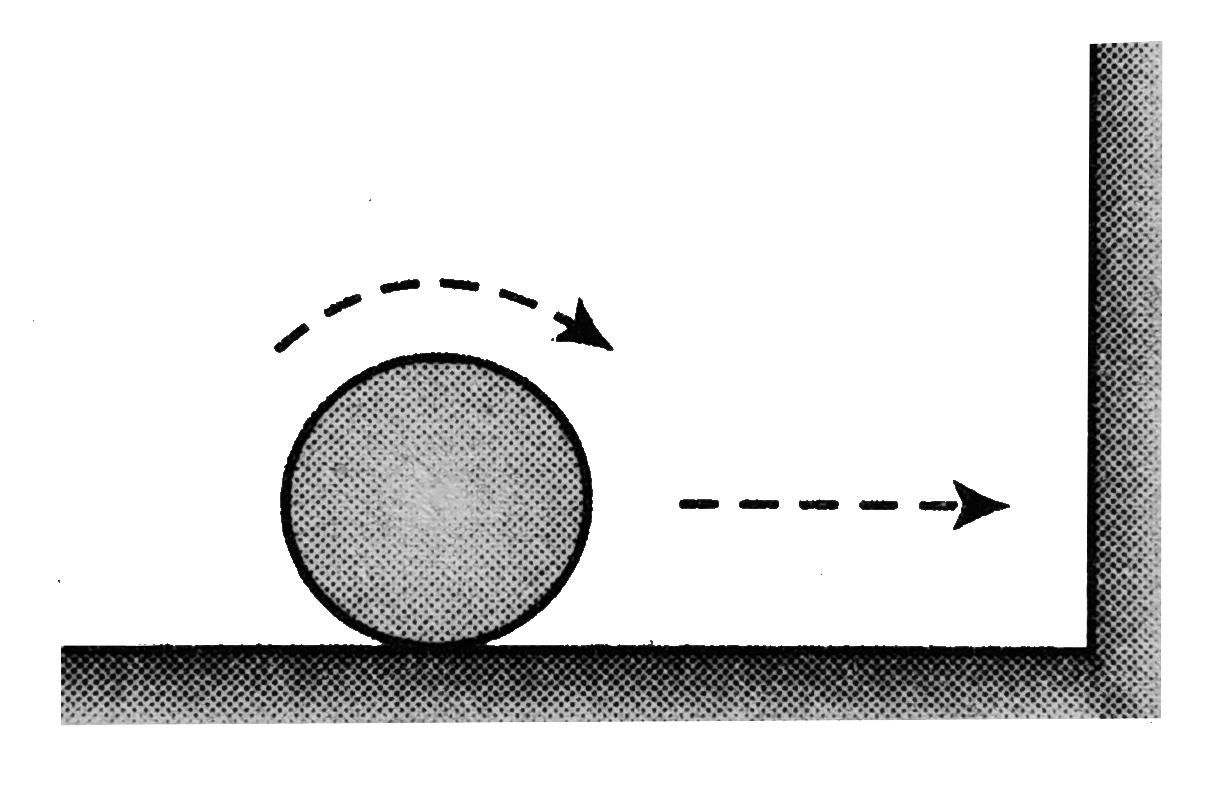
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|7 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Fill In The Blanks|7 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct|26 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|11 VideosSOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2-Linked Comprehension
- A solid cylinder of mass m is kept in balance on a fixed incline of an...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder of mass m is kept in balance on a fixed incline of an...
Text Solution
|
- A ball, rolling purely on a horizontal floor with centre's speed v, hi...
Text Solution
|
- A ball, rolling purely on a horizontal floor with centre's speed v, hi...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass 1 kg and radius 20 cm is rolling purely on a fl...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass 1 kg and radius 20 cm is rolling purely on a fl...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass 1 kg and radius 20 cm is rolling purely on a fl...
Text Solution
|
- In this passage a brief idea is given of the motion of the rolling bod...
Text Solution
|
- In this passage a brief idea is given of the motion of the rolling bod...
Text Solution
|
- In this passage a brief idea is given of the motion of the rolling bod...
Text Solution
|
- In this passage a brief idea is given of the motion of the rolling bod...
Text Solution
|
- A gardener presses the grasscutter with a force F at an angle theta. A...
Text Solution
|
- A gardener presses the grasscutter with a force F at an angle theta. A...
Text Solution
|
- A gardener presses the grasscutter with a force F at an angle theta. A...
Text Solution
|
- Two wheels A and C are connected by a belt B as shown in figure. The r...
Text Solution
|
- A solid ball of mass m and radius r spinning with angular velocity ome...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel A is connected to a second wheel B by means of inextensible st...
Text Solution
|
- Two forces of magnitude F are acting on a uniform disc kept on a horiz...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R is rolling purely on a flat horizontal, with a Cons...
Text Solution
|
- A boy is pushng a ring of mass 2kg and radius 0.5 m with a stick as sh...
Text Solution
|