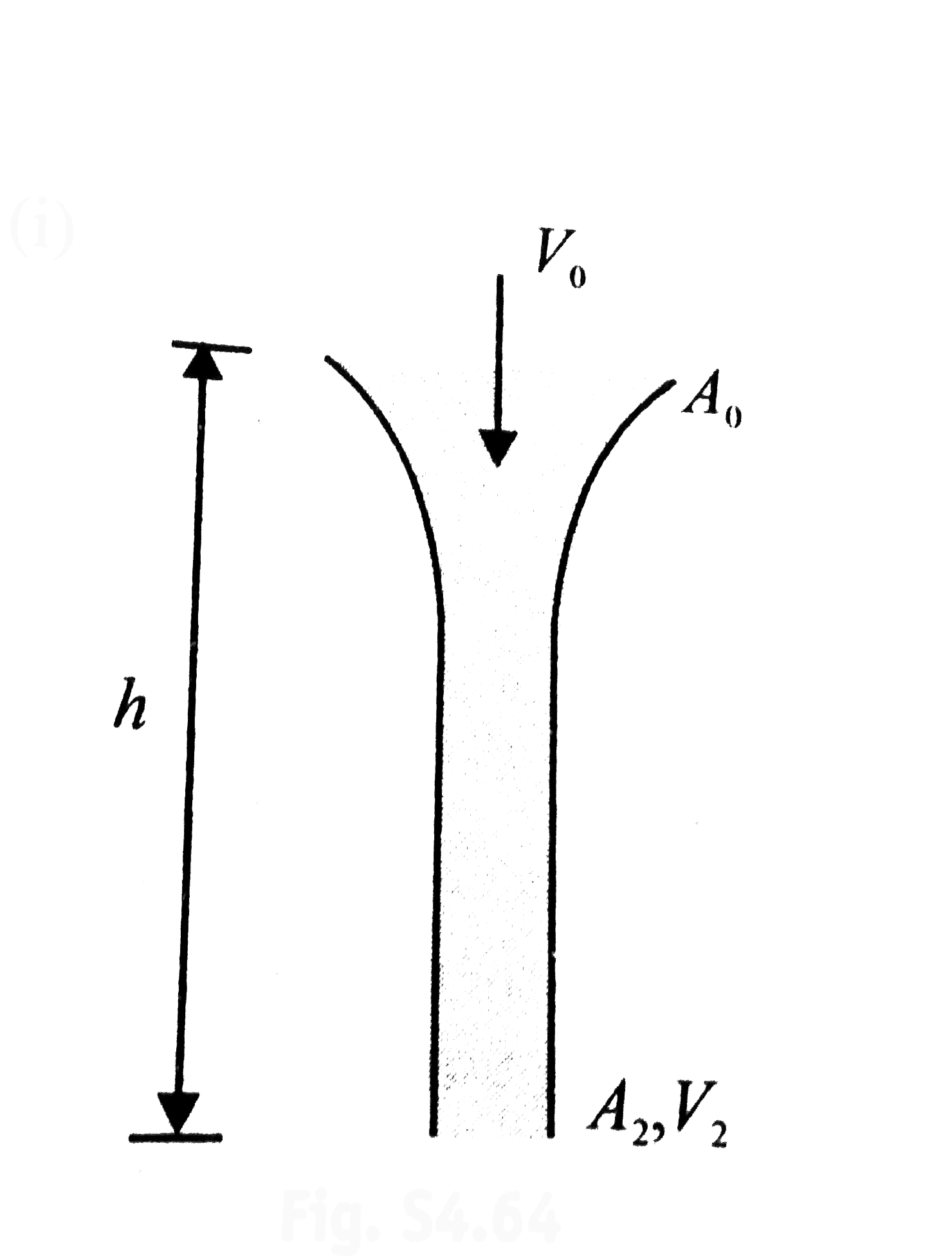A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
FLUID MECHANICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multipe Correct|15 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Assertion-Reasoning|8 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|25 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|2 VideosGRAVITATION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-FLUID MECHANICS-Single Correct
- Two unequal blocks placed over each other of densities sigma(1) and si...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement as shown, m(B)=3m, density of liquid is rho and den...
Text Solution
|
- Two wooden blocks A and B float in a liquid of density rho(L) as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Water from a tap emerges vertically downwards with an initial velocity...
Text Solution
|
- A large open tank has two holes in the wall. One is a square hole of s...
Text Solution
|
- A U tube is rotated about one of it's limbs with an angular velocity o...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement as shown, A and B arc two cylinders each of length ...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular vessel of dimension (lxxbxxh) and mass M contains a liqu...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a container filled with a liquid of density rho. Four poi...
Text Solution
|
- A circular cylinder of radius R and height H is filled with water to a...
Text Solution
|
- A small body of density rho' is dropped from rest at a height h into a...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical blocks each of mass m = 1 kg and volume 3 xx 10^(-4) m...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical vessel of 90 cm height is kept filled up to the brim. It...
Text Solution
|
- In the following figure shown, a liquid is filled into the vessel up t...
Text Solution
|
- An open vessel containing liquid is moving with constant acceleration ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical vessel of a very large cross sectional area is containin...
Text Solution
|
- A U-tube is held in a vertical plane such that its two limbs are verti...
Text Solution
|
- Equal volumes of a liquid are poured in the three vessels A, B and C (...
Text Solution
|
- If the system is not in free fall, which of the following, statements ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, an ideal liquid flows through the tube, which is of uni...
Text Solution
|