"An electrical machine used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy is known as A.C generatorialtermator".
Principle : It works on the principle of electromagnefic induction.
Construction : (1) Armature: Armature coil (ABCD) consists of a large number of turns of insulated copper wire wound Iron core over a soft iron core.
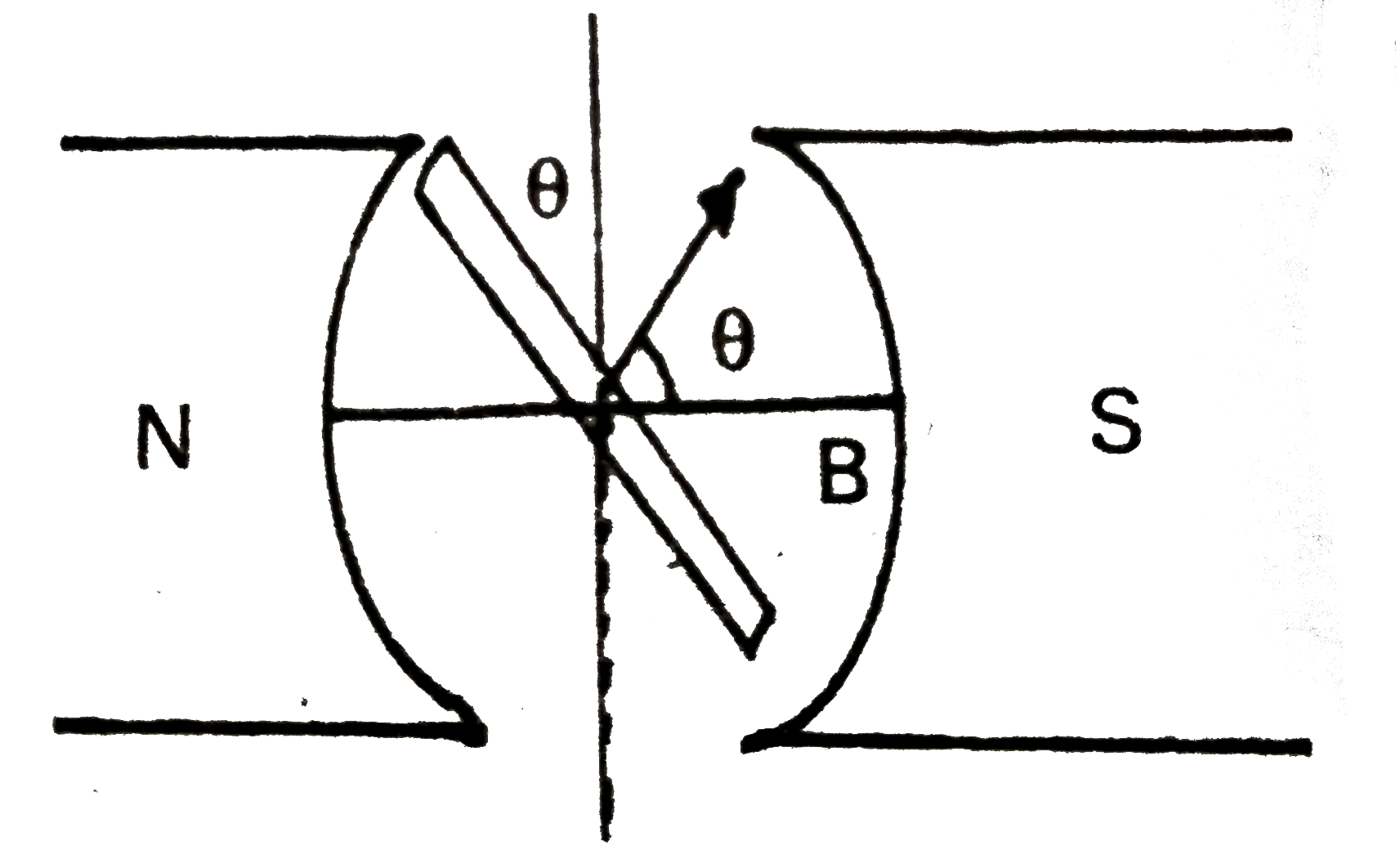
(ii) Strong field magnet : A strong permanent magnet (or) an electromagnet whose poles (N and S) are cylindrical in shape used as a field magnet. The armature coil rotates between the pole pieces of the field magnet.
(iii) Slip rings : The two ends of the armature coil are connected to two brass slip rings `R_1 and R_2` These rings rotate along with the armature coil.
(iv) Brushes : Two carbon brushes `B_1 and B_2` are pressed against the slip rings. The brushes remain fixed while slip rings rotate along with the armature. These brushes are connected to the load through which the out put is obtained.
Working : When the armature coil ABCD rotates is the magnetic field provided by the strong field magnet, it cuts the magnetic line of force. The magnetic flux linked with the coil changes due to the rotation of the armature and hence induced e.m.f is set up in the coil.
The current flows out through the brush B in one direction of half of revolution and through the brush B, in the next half revolution in the reverse direction. This process is repeated, therefore e m.f produced is of alternating nature
Theory:
(i) When the coil is rotated with a constant angular velocity `(omega)`
(ii) The angle between the normal to the eoil and magnetic field `vecB` at any instant is given by `theta=omegat ..(1)`

The component of magnetic field normal to the plane of the coil `=B cos theta= B cos omegat` .....(2)
(iv) Magnetic flux linked with the single turn of the coil `=(B cos omegt)A ......(3)`
where A is the area of the coil, if the coil has n turns
(v) Total magnetic flux linked with the coil `(phi)=n(B cos omegat)A`
According to Faraday's law.
`epsi=-(d phi)/(dt)=-(dt)/(dt)(nBA cos omegat)=-nBA(-omega sin omegat)`
`epsi=nBA omega sinomegat.....(5)`
Where `nBAomega` is the maximum value of e.m.f. `(epsi_(0))`
`I=(epsi)/(R)=(epsi)/(R)=sin omegat " "(therefore i=(epsi_(0))/(R))`
`I=I_(0) sin omegat`
The direction of the current changes periodically and therefore the current is called alternating current (a.c.)