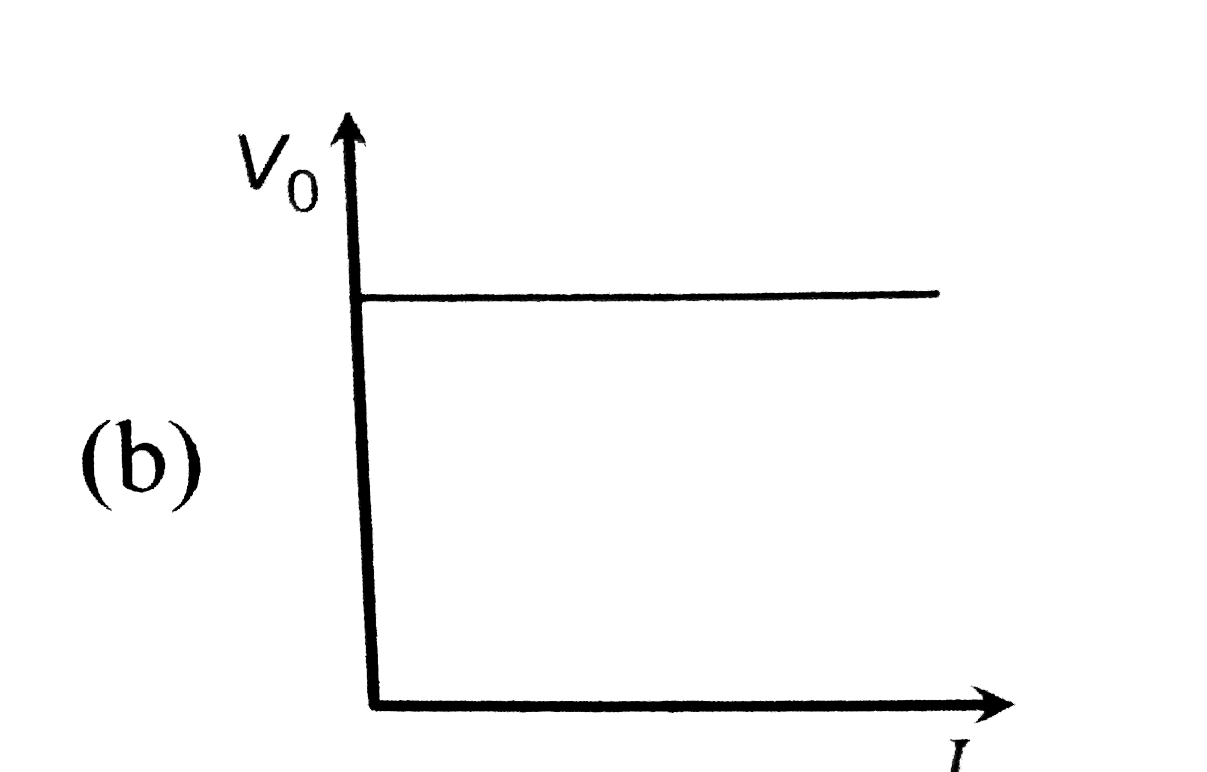
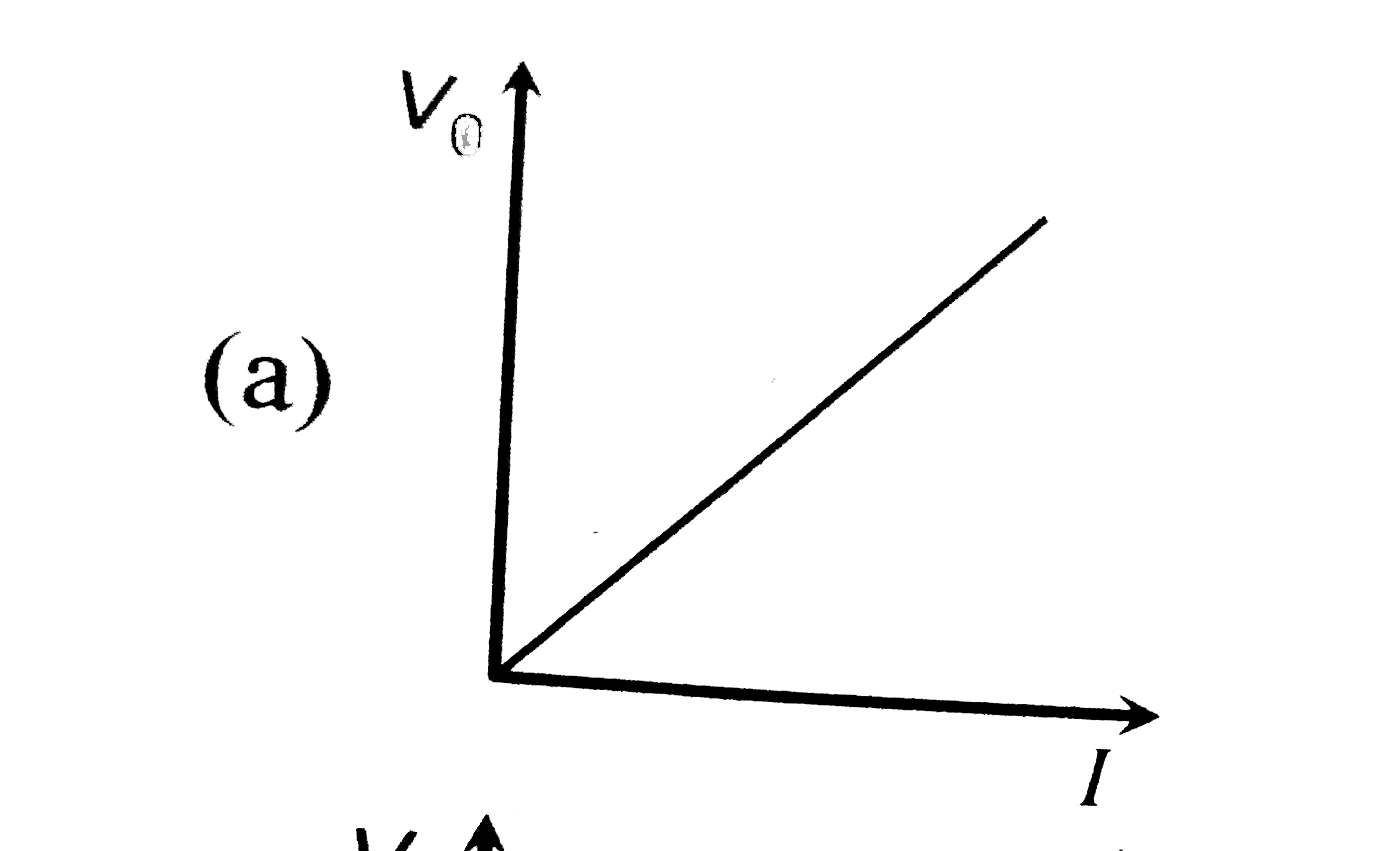
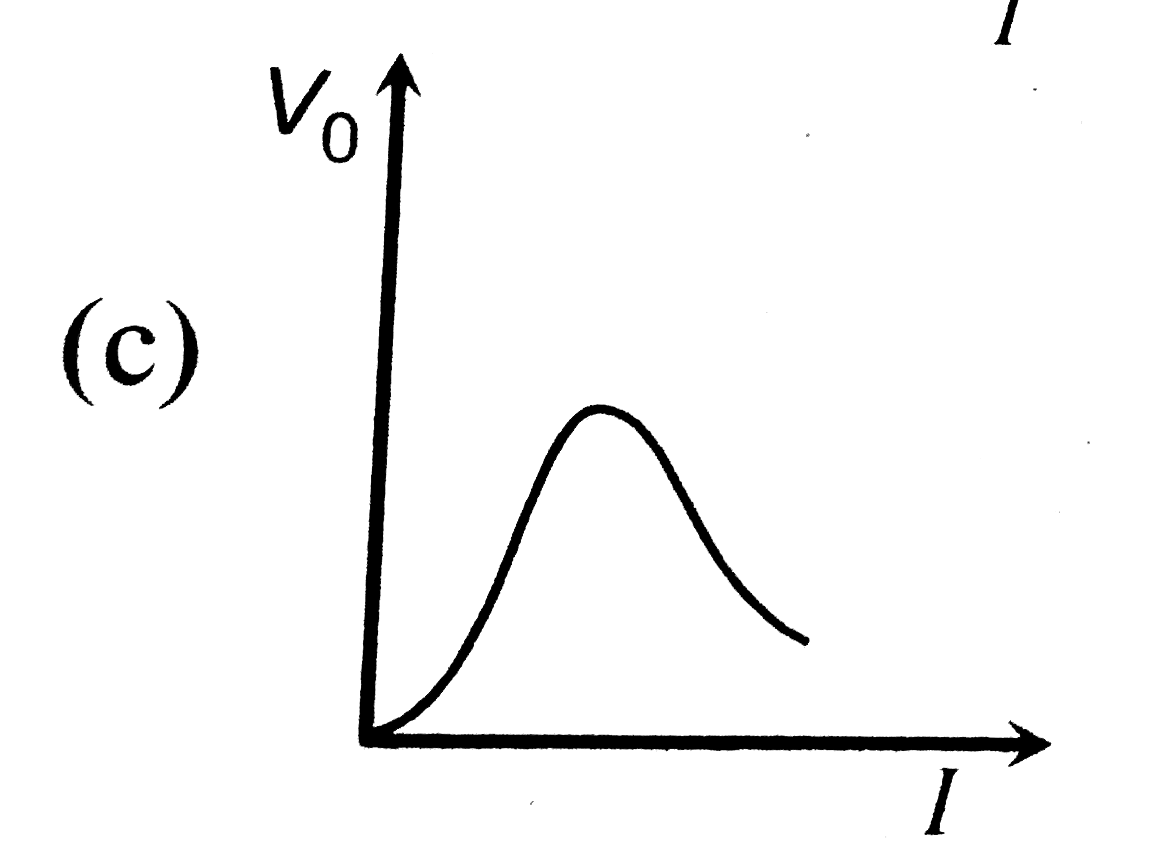
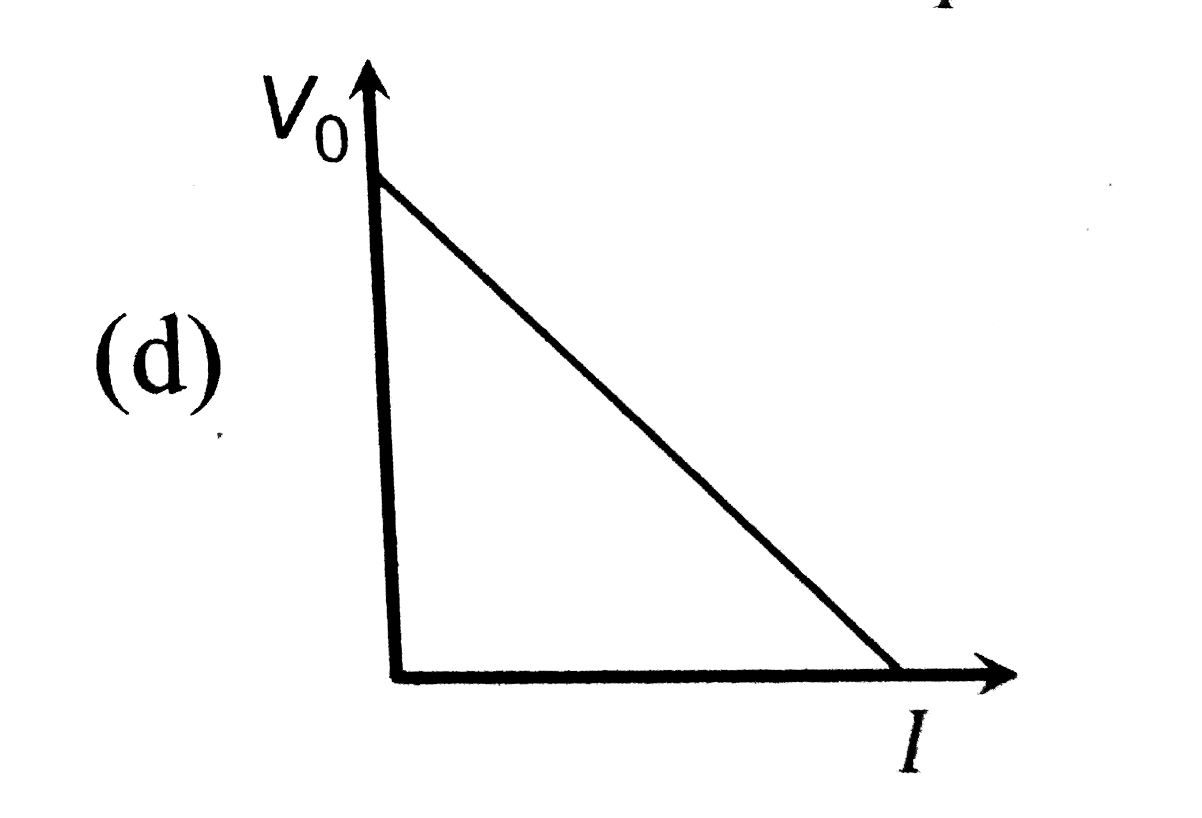
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
A2Z|Exercise Section B - Assertion Reasoning|18 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
A2Z|Exercise AIPMT/NEET Questions|46 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
A2Z|Exercise X-Rays|45 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|29 VideosELECTRIC CHARGE, FIELD & FLUX
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|29 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER-Problems Based On Mixed Concepts
- Light from a hydrogen tube is incident on the cathode of a photoelectr...
Text Solution
|
- Work function of lithium and copper are respectively 2.3 eV and 4.0 eV...
Text Solution
|
- The largest distance between the interatomic planes of crystal is 10^(...
Text Solution
|
- Find the ratio of de Broglie wavelength of molecules of hydrogen and h...
Text Solution
|
- A silver of radius 4.8 cm is suspended by a thread in the vacuum chamb...
Text Solution
|
- A photon of wavelength 6630 Å is incident on a totally reflecting surf...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of de - Broglie wavelength of alpha - particle to that of a ...
Text Solution
|
- Kalpha wavelength emitted by an atom of atomic number Z=11 is lambda. ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy of a partical varies as . U(x) = E0 for 0 le x...
Text Solution
|
- In order to coincide the parabolas formed by singly ionized ions in on...
Text Solution
|
- In a photocell bichromatic light of wavelength 2475 Å and 6000 Å are i...
Text Solution
|
- Two metallic plate A and B , each of area 5 xx 10^(-4)m^(2), are place...
Text Solution
|
- In the following arrangement y = 1.0 mm , d = 0.24 mm and D = 1.2 m. T...
Text Solution
|
- The eye can detect 5xx10^(4) photons (m^2s)^(-1) of green light (lamda...
Text Solution
|
- A photon collides with a stationary hydrogen atom in ground state inel...
Text Solution
|
- The curve between current (i) and potential difference (V) for a phot...
Text Solution
|
- The correct curve between the stopping potential (V) and intensity of ...
Text Solution
|
- The value of stopping potential in the following diagram
Text Solution
|
- In the following diagram if V(2) gt V(1) then
Text Solution
|
- The correct graph between the maximum energy of a photoelectron and th...
Text Solution
|