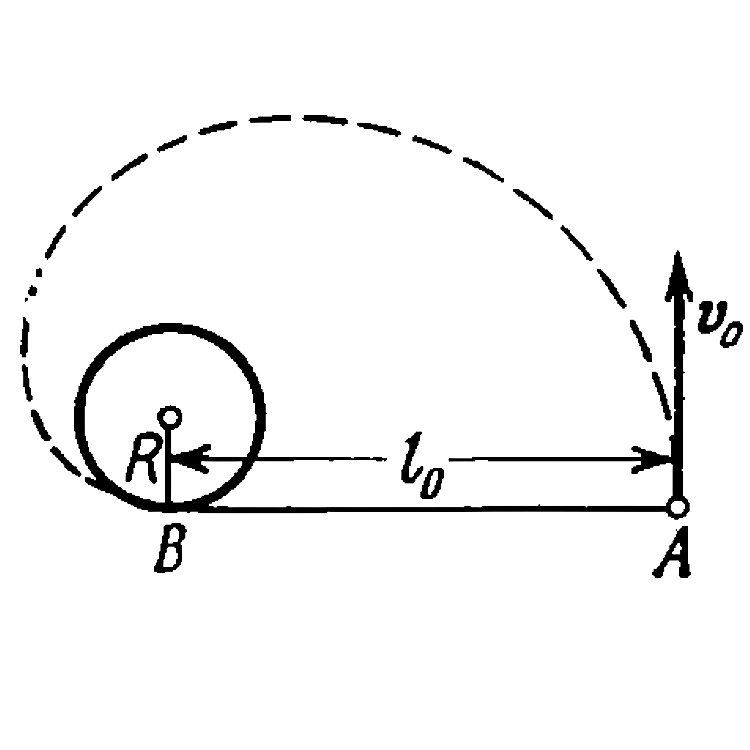
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Universal Gravitation|34 VideosPHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Dynamics Of A Solid Body|56 VideosPHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise The Fundamental Equation Of Dynamics|59 VideosOSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Electromagnetic Waves, Radiation|36 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS AND MOLECULAR PHYSICS
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV|Exercise Transport Phenomena|38 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
IE IRODOV, LA SENA & SS KROTOV-PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS-Laws Of Conservation Of Energy, Momentum And Angular Momentum
- A small body A starts sliding from the height h down an inclined groov...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is suspended by a thread of length l. With what minim...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal plane supports a stationary vertical cylinder of radius R...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth rubber cord of length l whose coefficient of elasticity is k ...
Text Solution
|
- A small bar A resting on a smooth horizontal plane is attached by thre...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal plane supports a plank with a bar of mass m=1.0kg placed ...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth light horizontal rod AB can rotate about a vertical axis pass...
Text Solution
|
- A pulley fixed to the ceiling carries a thread with bodies of masses m...
Text Solution
|
- Two interacting particles from a closed system whose centre of inertia...
Text Solution
|
- A closed chian A of mass m=0.36kg is attached to a vertical rotating s...
Text Solution
|
- A round cone A of mass m=3.2kg and half-angle alpha=10^@ rolls uniform...
Text Solution
|
- In the reference frame K two particles travel along the x axis, one of...
Text Solution
|
- The reference frame, in which the centre of inertia of a given system ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small discs of masses m1 and m2 interconnected by a weightless spr...
Text Solution
|
- A system consists of two small spheres of masses m1 and m2 interconnec...
Text Solution
|
- Two bars of masses m1 and m2 connected by a weightless spring of stiff...
Text Solution
|
- Two bars connected by a weightless spring of stiffness ϰ and length (i...
Text Solution
|
- A system consists of two identical cubes, each of mass m, linked toget...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical buggies 1 and 2 with one man in each move without fricti...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical buggies move one after the other due to inertia (without...
Text Solution
|