A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-CIRCULAR MOTION-LEVEL-VI
- A small bead of mass m is carried by a circular hoop having center at ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical particles are attached at the end of a light string whic...
Text Solution
|
- For the arrangement in the Figure, the particle M(1) attached to one e...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B separated by a distance 2R are moving counter cl...
Text Solution
|
- A bead of mass m is located on a parabolic wire with its axis vertical...
Text Solution
|
- A mass 1kg attached to the end of a flexible rope of diameter d = 0.25...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, a smooth parabolic wire track lies in the xy-plan...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R has a light pole fixed perpendicular to the disc at...
Text Solution
|
- A particle travels along the arc of a circle of radius r. Its speed de...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving in a circle of radius R in such a way that at any...
Text Solution
|
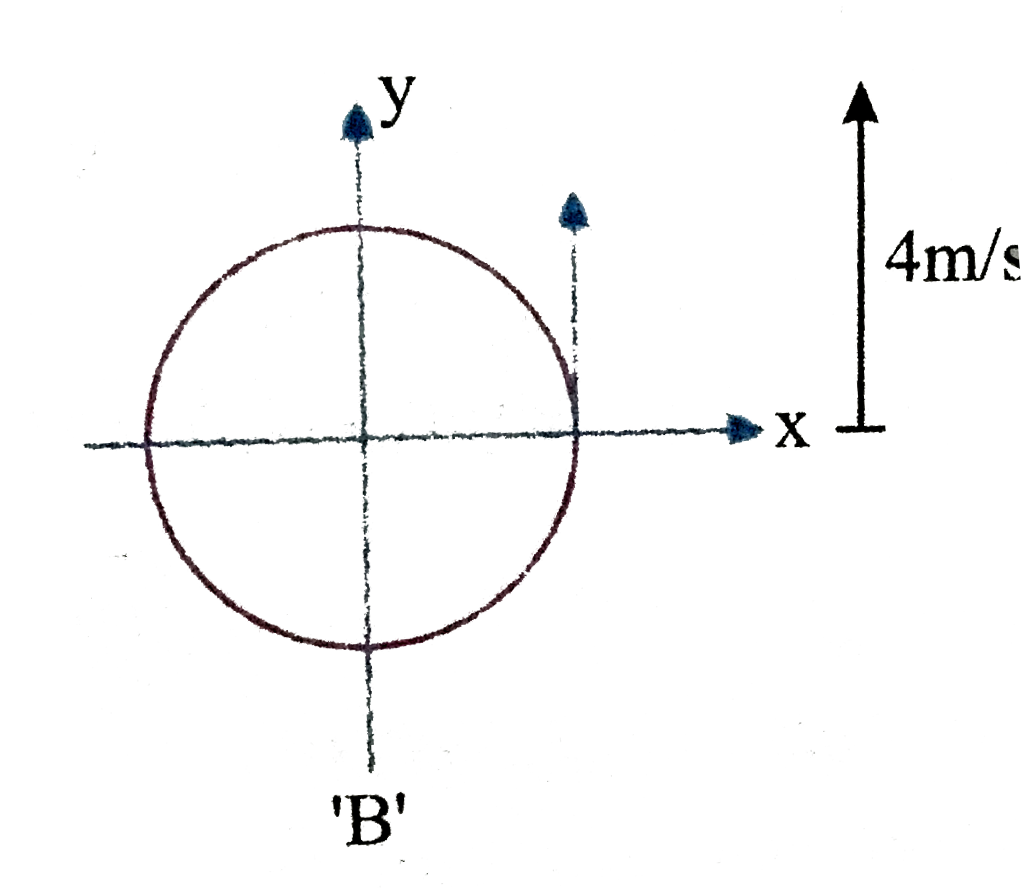
- Particle A moves with 4m//s along positive y-axis and particle B in a ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle 'A' moves along a circle with a velocity v=at, where a=0.5...
Text Solution
|
- A particle P of mass m is attached to a vertical axis by two strings A...
Text Solution
|
- A body moves on a horizontal circular road of radius r, with a tangent...
Text Solution
|