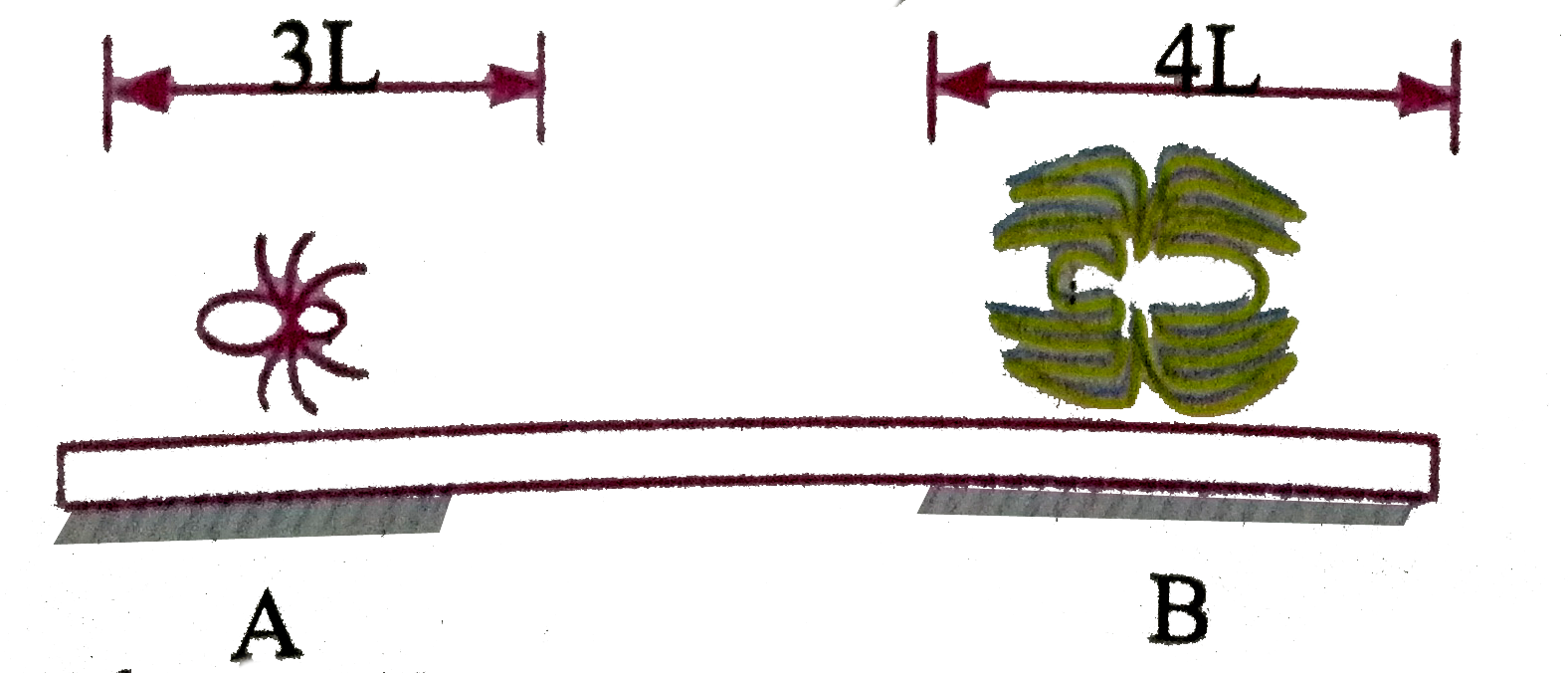
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-COLLISION-Comprehension type
- Wedges B and C are smooth and they are placed in contact as shown. Blo...
Text Solution
|
- Wedges B and C are smooth and they are placed in contact as shown. Blo...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 12 L and mass 48 m is supported horizontally o...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 12 L and mass 48 m is supported horizontally o...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 12 L and mass 48 m is supported horizontally o...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile of mass 50 kg is shot vertically upwards with n initial v...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile of mass 50 kg is shot vertically upwards with n initial v...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile of mass 50 kg is shot vertically upwards with n initial v...
Text Solution
|
- A small particle of mass m//10 is moving horizontally at a height of 3...
Text Solution
|
- A small particle of mass m//10 is moving horizontally at a height of 3...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth balls A and B, each of mass m and radius R, have their cent...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth balls A and B, each of mass m and radius R, have their cent...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth balls A and B, each of mass m and radius R, have their cent...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth balls A and B, each of mass m and radius R, have their cent...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is projected with a velocity 'u' at angle theta with ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is projected with a velocity 'u' at angle theta with ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is projected with a velocity 'u' at angle theta with ...
Text Solution
|
- An inelastic ball is projetced with a velocity 'u' at an angle 'alpha'...
Text Solution
|
- An inelastic ball is projetced with a velocity 'u' at an angle 'alpha'...
Text Solution
|
- An inelastic ball is projetced with a velocity 'u' at an angle 'alpha'...
Text Solution
|