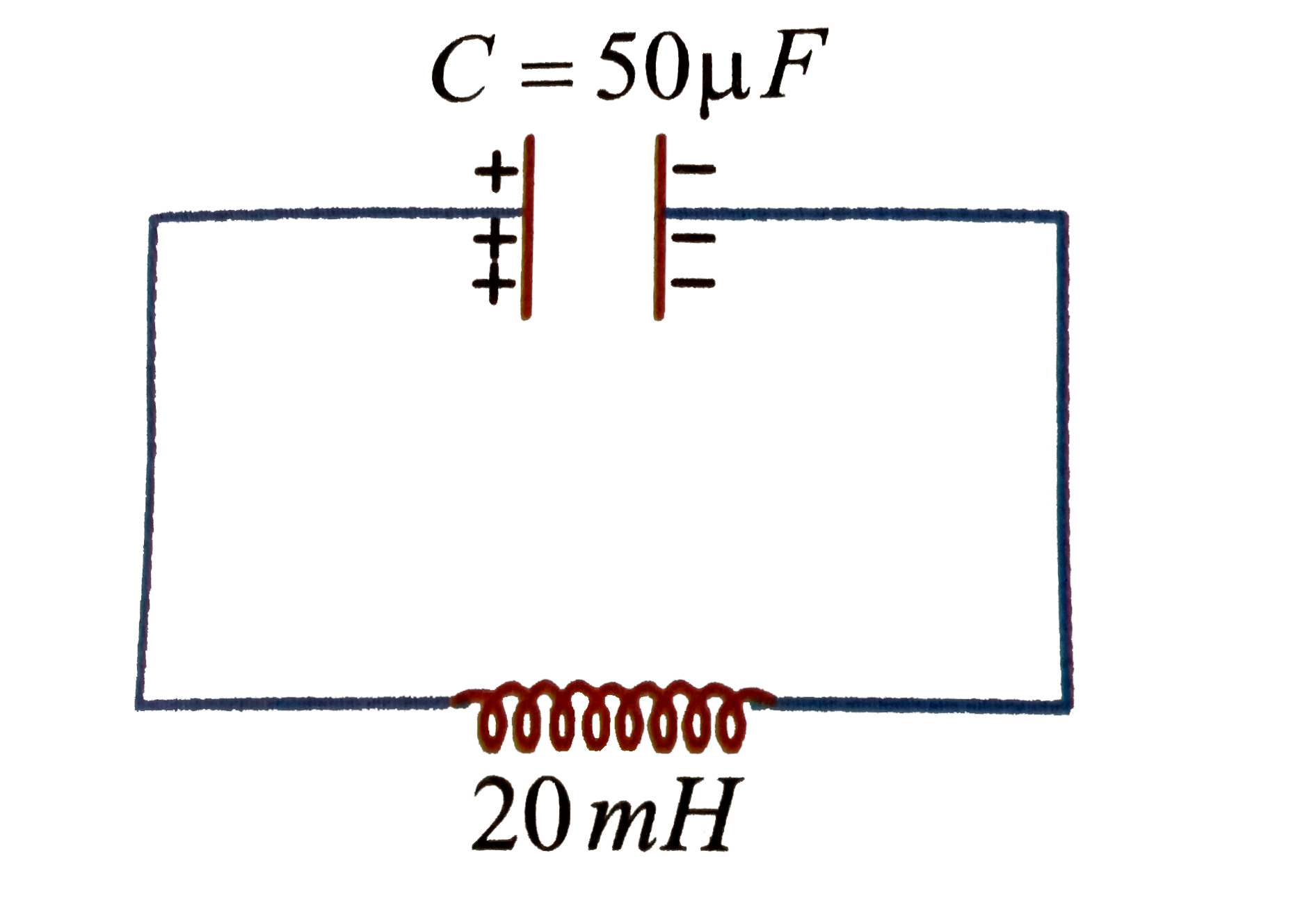
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARAYNA-ALTERNATING CURRENT-LEVEL - IV NCERT Based Questions
- If the rms current in a 50 Hz ac circuit is 5 A, the value of the cur...
Text Solution
|
- An alternating current generator has an internal resistance R(g) and a...
Text Solution
|
- When a voltage measuring device is connected to a.c. mains the meter s...
Text Solution
|
- To reduce the resonant frequency in an LCR series circuit with a gener...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following combinations should be selected for better turn...
Text Solution
|
- A inductor of reactance 1 Omega and a resistor of 2 Omega are connecte...
Text Solution
|
- The output of a step-down transformer is measured to be 24 V when conn...
Text Solution
|
- As the frequency of an ac circuit increases, the current first increas...
Text Solution
|
- In an alternating current circuit consisting of elements in series, th...
Text Solution
|
- Electrical energy is transmitted over large distances at high alternat...
Text Solution
|
- For an LCR circuit, the power transferred from the driving source to t...
Text Solution
|
- When an A.C voltage of 220 V is applied to the capacitor C
Text Solution
|
- The line the draws power supply to your house from street has
Text Solution
|
- An LC circuit contains a 20 mH inductor asn a 50 mu F capacitor with i...
Text Solution
|
- If the three elements, L,C and R are arranged in parallel. Source has ...
Text Solution
|