Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT QUESTIONS AND EXERCISES WITH ANSWERS (NCERT INTEXT UNSOLVED QUESTIONS)|9 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT QUESTIONS AND EXERCISES WITH ANSWERS (NCERT EXERCISES)|22 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
PRADEEP|Exercise CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS|26 VideosGENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS
PRADEEP|Exercise Curiosity Questions|2 VideosORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN
PRADEEP|Exercise IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR BOARD EXAMINATION|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-NCERT QUESTIONS AND EXERCISES WITH ANSWERS (NCERT INTEXT SOLVED QUESTIONS)
- Draw the structures of all the eight structural isomers that have the ...
Text Solution
|
- Write IUPAC anmes of the following:
Text Solution
|
- Identify all the possible monochloro structural isomers expected to be...
Text Solution
|
- Write the products of the following reactions:
Text Solution
|
- Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as main product whil...
Text Solution
|
- In the following pairs of halogen compounds which is faster undergoing...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the order of reactivity of the following compounds in S (N)1 a...
Text Solution
|
- Identify chiral and achiral molecules in each of the following pairs c...
Text Solution
|
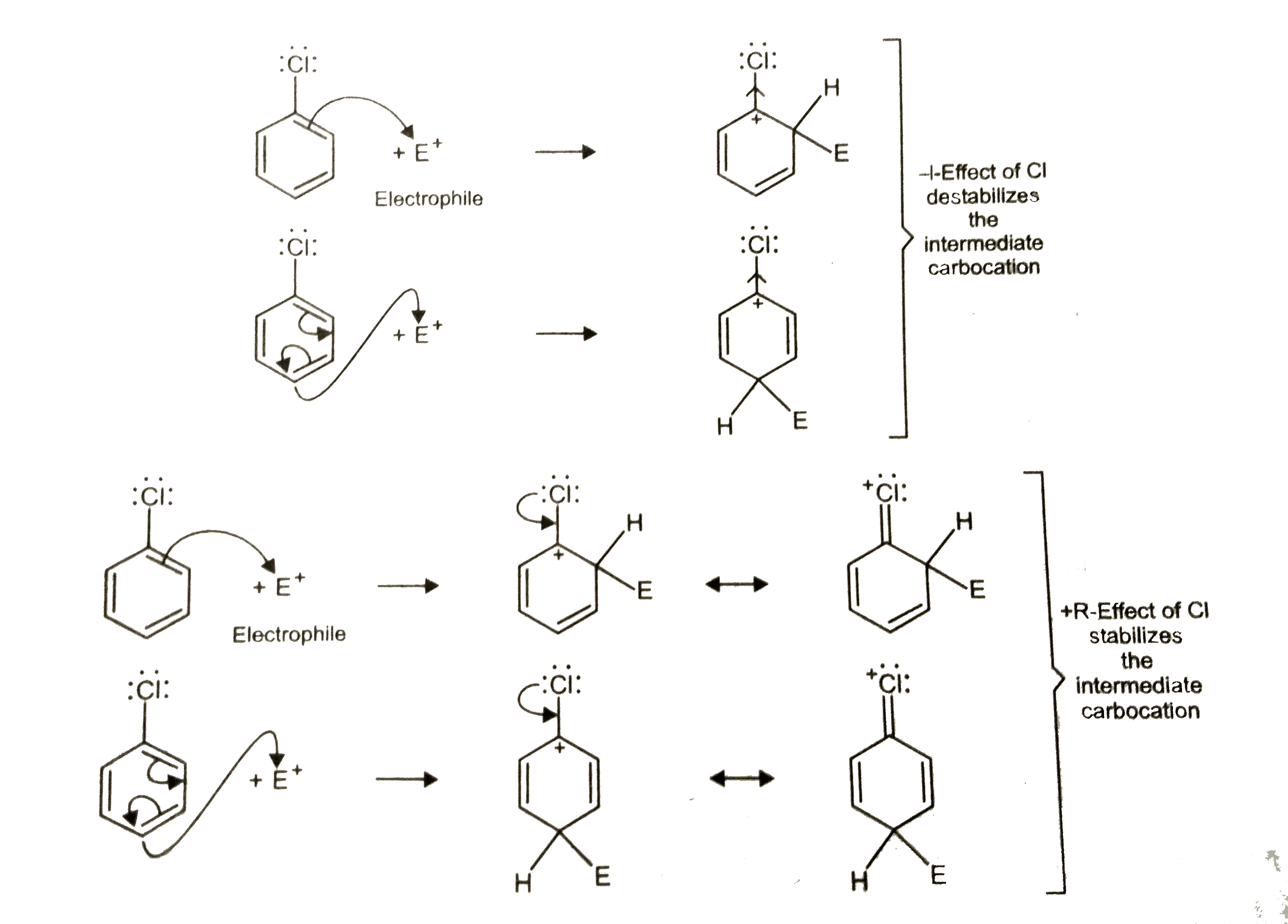
- Although chlorine is an electron-withdrawing group, yet it is ortho-, ...
Text Solution
|