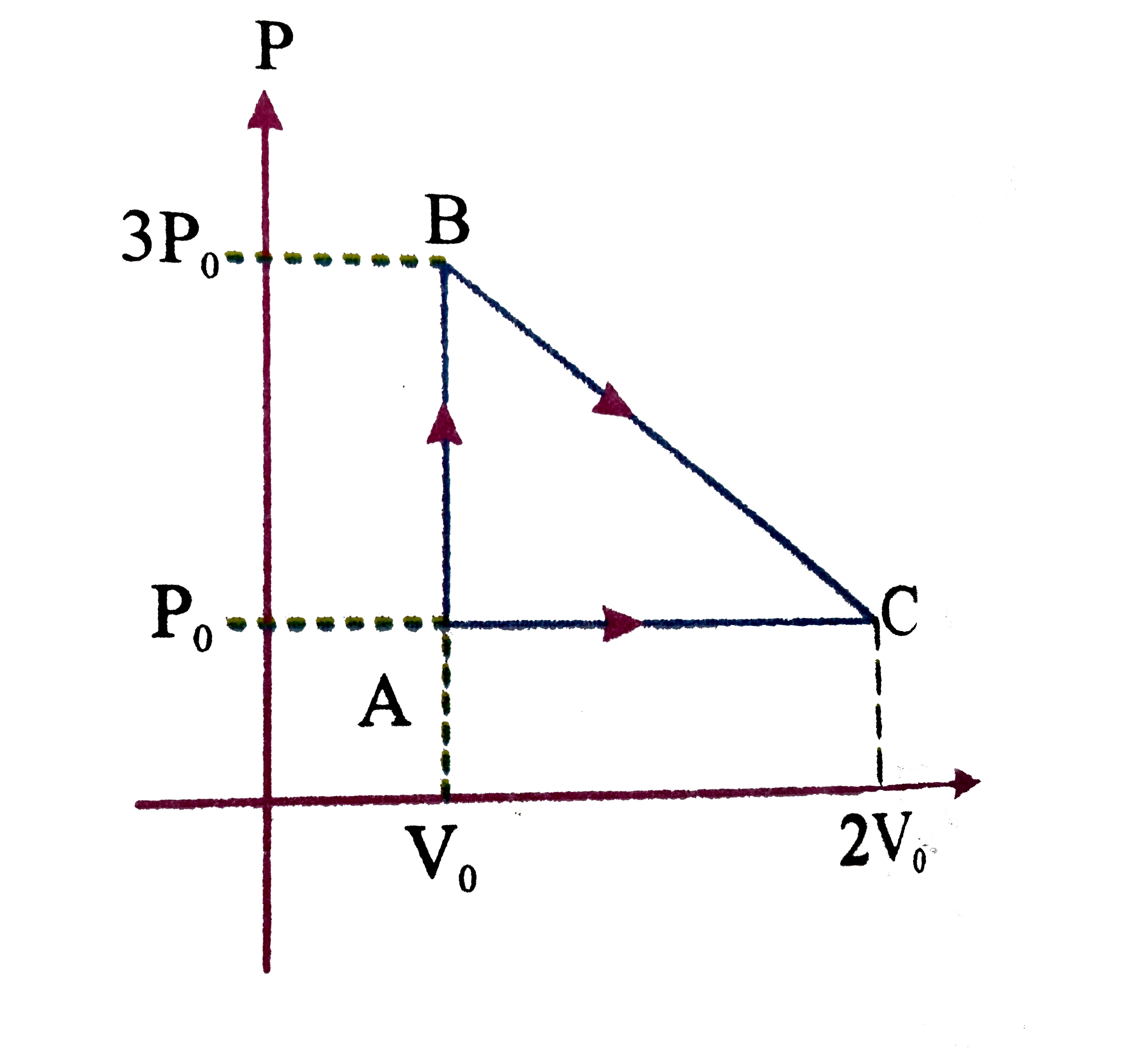
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-KTG & THERMODYNAMICS-SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
- A sample of 2 kg of monatomic helium (assumed ideal) is taken through ...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas are confined within a cylinder by...
Text Solution
|
- Two vessels A and B, thermally insulated, contain an ideal monoatomic ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a diatomic ideal gas (gamma=1.4) is taken through a cyclic...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, an ideal gas changes it state from A to state C b...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal monoatomatic gas is taken round the cylic process...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas, initially at pressure p1 and vol...
Text Solution
|
- A weightless piston divides a thermally insulated cylinder into two pa...
Text Solution
|
- Two containers A and B of equal volume V(0)//2 each are connected by a...
Text Solution
|
- In given figure, an adiabatic cylindrical tube of volume 2V(0) is divi...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure a glass tube lies horizontally with the middle 20c...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical tube with adiabatic walls having volume 2V(0)contains an...
Text Solution
|
- A mass of 8g of oxygen at the pressure of one atmosphere and at temper...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas ((C(p))/(C(v))=gamma)has initial volume V(0) is kept in a...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas (C(p)//C(v) =gamma) having initial pressure P(0) and volu...
Text Solution
|
- An insulting container of volume 2V(0) is divided in two equal parts b...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas (gamma=3//2) is compressed adiabatically form volume 400c...
Text Solution
|
- Two samples A and B of the same gas have equal volumes and pressure. T...
Text Solution
|
- A Carnot engine cycle is shown in the Fig. (2). The cycle runs between...
Text Solution
|
- Cloud formation condition Consider a simplified model of cloub forma...
Text Solution
|