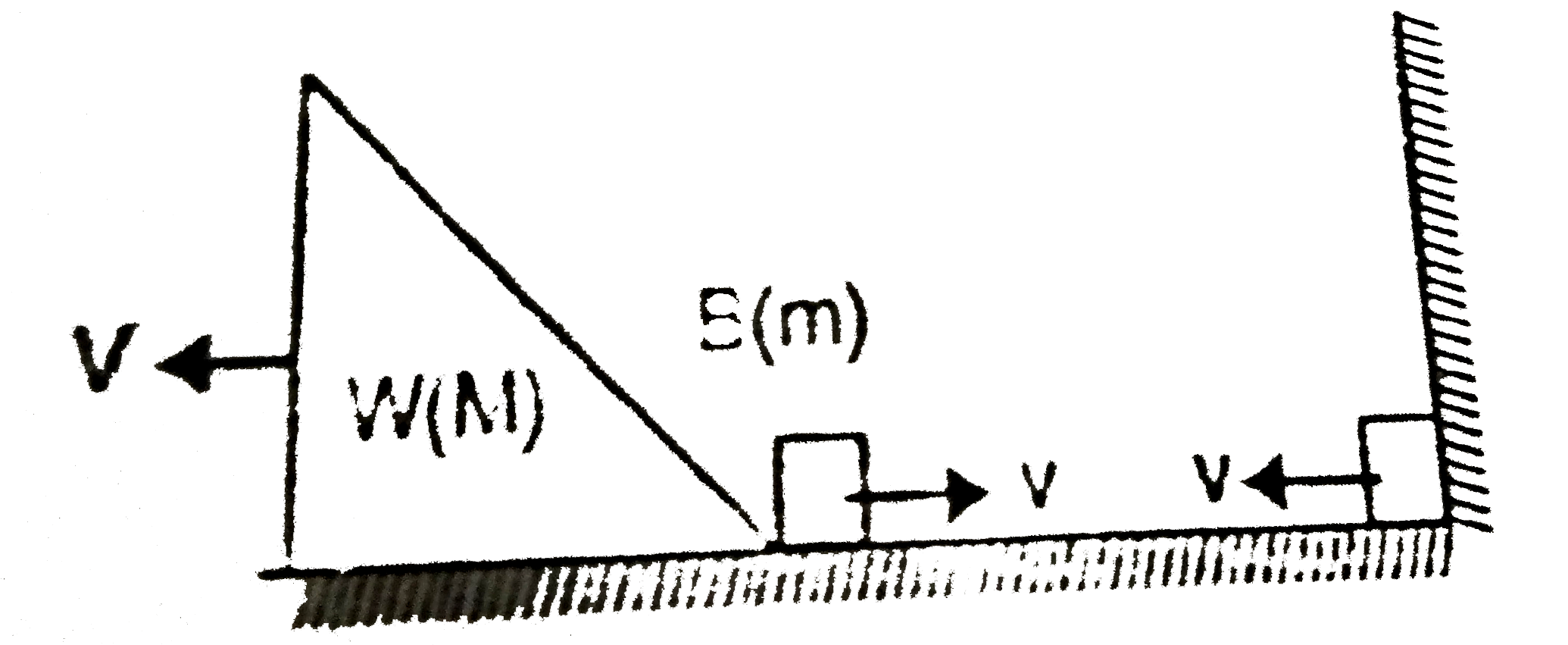A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 58|9 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 59|5 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE|Exercise dpp 56|7 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise|54 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-dpp 57
- The moment of inertia of a door of mass m, length 2 l and width l abou...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of equal masses are attached to a string passing ov...
Text Solution
|
- Three point masses are arranged as shown in the figure. Moment of iner...
Text Solution
|
- A section of fixed smooth circular track of radius R in vertical plane...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, the block B of mass m starts from rest at the top of a ...
Text Solution
|
- In a free space a rifle on mass M shoots a bullet of mass m at a stati...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular chain of radius r and mass m rests over a sphere of...
Text Solution
|