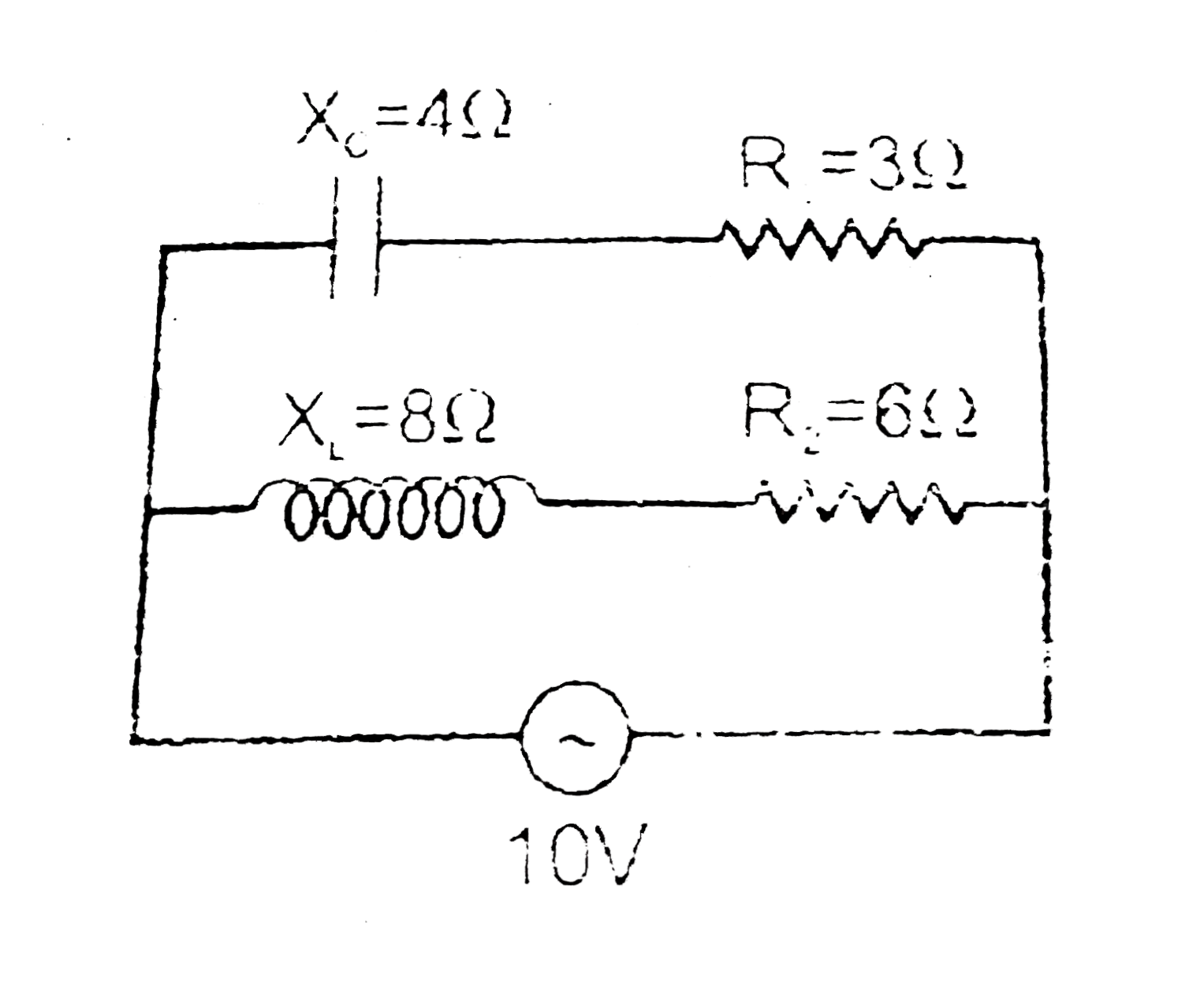Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE|Exercise DPP No.56|20 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE|Exercise DPP No.57|9 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE|Exercise DPP No.54|9 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE|Exercise High Level Problems (HIP)|21 VideosELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVES
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise 3|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM-DPP No.55
- The circuit was in the shown state for a long time. Now if the switch ...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charge +q and -q are fixed on diameterically opposite point ...
Text Solution
|
- A 10m long potentiometer wire has a resistance of 20 ohm. It is connec...
Text Solution
|
- Monochromatic light of wavelength lamda passes through a very narrow s...
Text Solution
|
- Three 200 Omega resistors are connected as shown in figure. The maximu...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown an ideal alternative current (A,C) source of 10 Vo...
Text Solution
|
- A small particle of mass m = 1 kg and charge of 1C enters perpendicula...
Text Solution
|
- A small particle of mass m = 1 kg and charge of 1C enters perpendicula...
Text Solution
|
- A small particle of mass m = 1 kg and charge of 1C enters perpendicula...
Text Solution
|