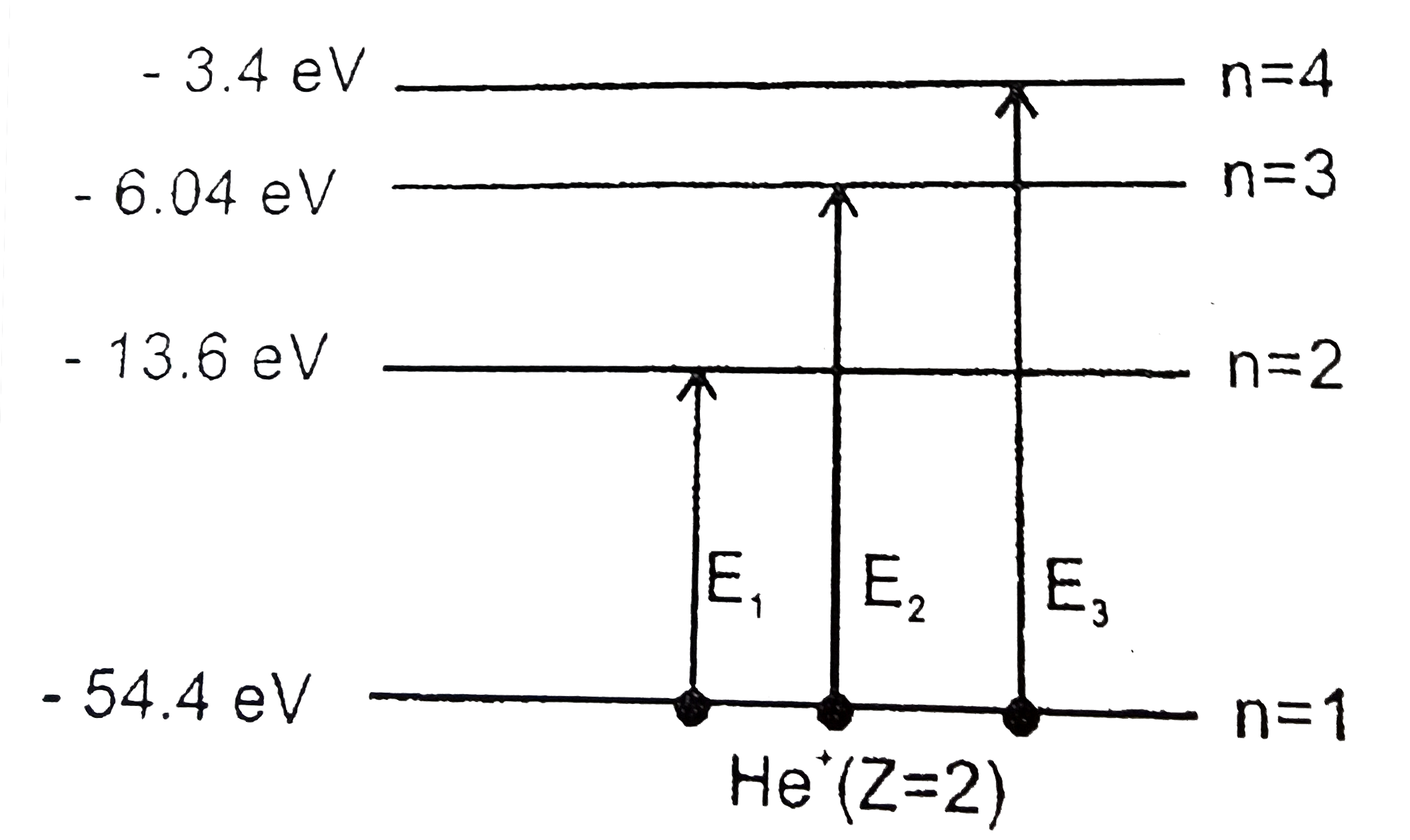
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-ATOMIC PHYSICS-Advanved level problems
- A small particle of mass m move in such a way the potential energy (U ...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the potential energy between an electron and aproton at a dist...
Text Solution
|
- In atension from state n to a state of excitation energy 10.19 eV, hyd...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose in certine condition only those transition are allowed to hydr...
Text Solution
|
- Find the velocity of photoelectrons liberated by electromagnetic radia...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Find the maximum wavelength lambda(0) of light which can ionize a ...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of monochromatic light of wavelength lambda ejects photoelectro...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrogen atom in its good state is excited by means of monochromatic r...
Text Solution
|
- Average lifetime of a hydrogen atom excited to n =2 state is 10^(-6)s ...
Text Solution
|
- In a hydrogen like ionized atom a single electron is orbiting around ...
Text Solution
|
- For atoms of light and heavy hydrogen (H and D) fine the difference, ...
Text Solution
|
- An electron in the ground state of hydrogen atom is revolving in antic...
Text Solution
|
- A proton and electron, both at rest initially, combine to form a hydro...
Text Solution
|
- A neutron of kinetic 6.5 eV collides inelastically with a singly ioniz...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the potential energy between electron and proton at a distance...
Text Solution
|
- A positronium consists of an electron and a positron revolving about t...
Text Solution
|
- In a photoelectric effect set up, a point source of light of power 3.2...
Text Solution
|