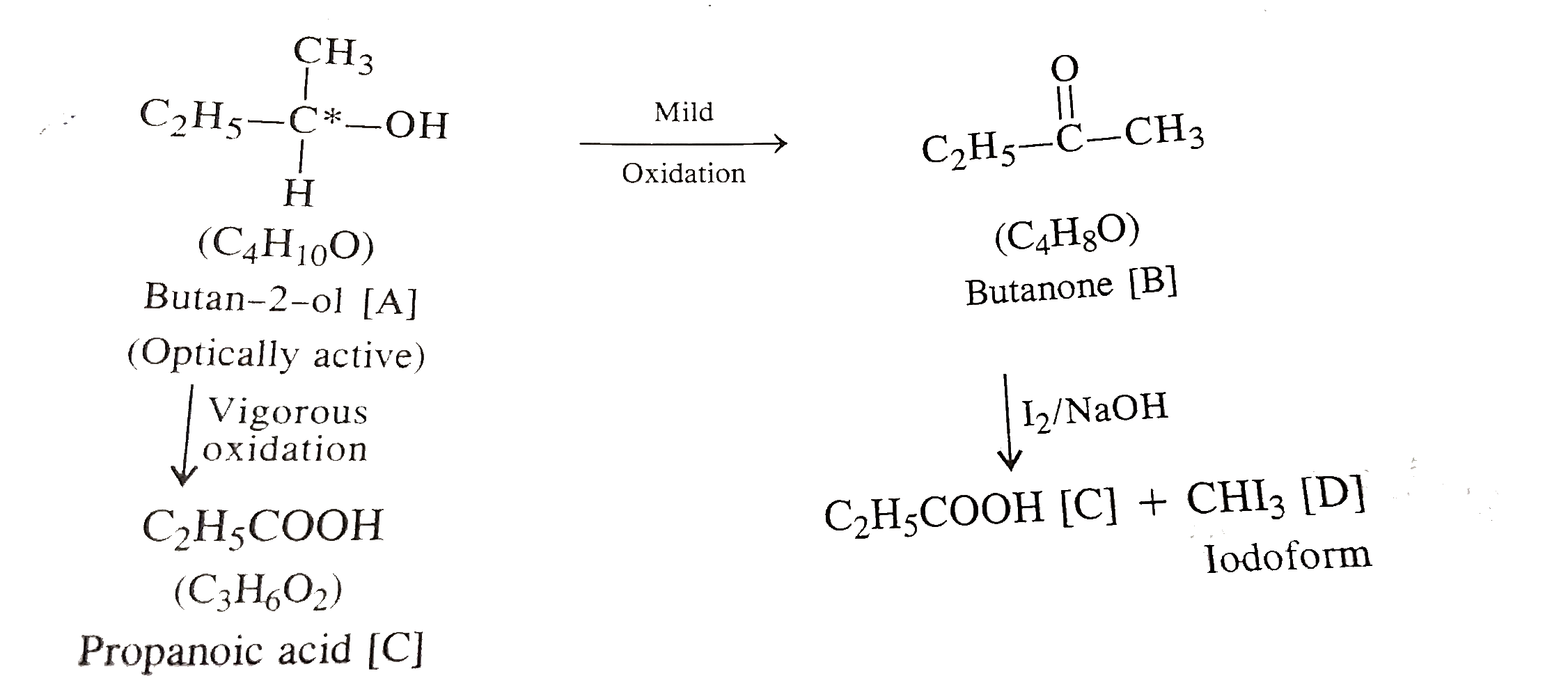Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Additional Important Question|35 VideosALDEHYDES AND KETONES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Question From Board|86 VideosALDEHYDES AND KETONES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Interger|5 VideosALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Matrix|9 VideosALKALI EARTH METALS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit test-12|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DINESH PUBLICATION-ALDEHYDES AND KETONES -Problem
- An alkane A on ozobolysis yields acetone and an aldeyde. The aldehyde ...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound 'A' (C(4)H(10)O) is optically active. On mild oxid...
Text Solution
|
- A compound [A] with molecular formula C(5)H(10)O gave a positive 2,4-D...
Text Solution
|
- A compound [A] of molecular formula C(4)H(9)Br yields a compound [B] o...
Text Solution
|
- A ketone A, which undergoes halform reaction, gives compound B on redu...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound [A] with molecular formula C(4)H(8)O when reduced ...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrocarbon (X), C(7)H(12), on reaction with boron hydride followed by...
Text Solution
|
- An alkane (A) C(16)H(16) on ozonolysisi gives only one products (B) C(...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound [A] C(8)H(6) on reacting with dilute sulphuric aci...
Text Solution
|
- An unknown aldehyde [A] on reacting with alkali gives beta-hydroxyalde...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound [A] with molecular formula C(5)H(8)O(2) is reduced...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compoud [A] which has characteristic odour on treatment wit...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound 'A' (molecular formula C(4)H(10)O) reacts vigorusl...
Text Solution
|
- An aldehyde (A) (C(11)H(8)O), which does not undergo self aldol conden...
Text Solution
|
- (A), (B) and (C ) are three non-cylic funtional isomers of a carbonyl ...
Text Solution
|