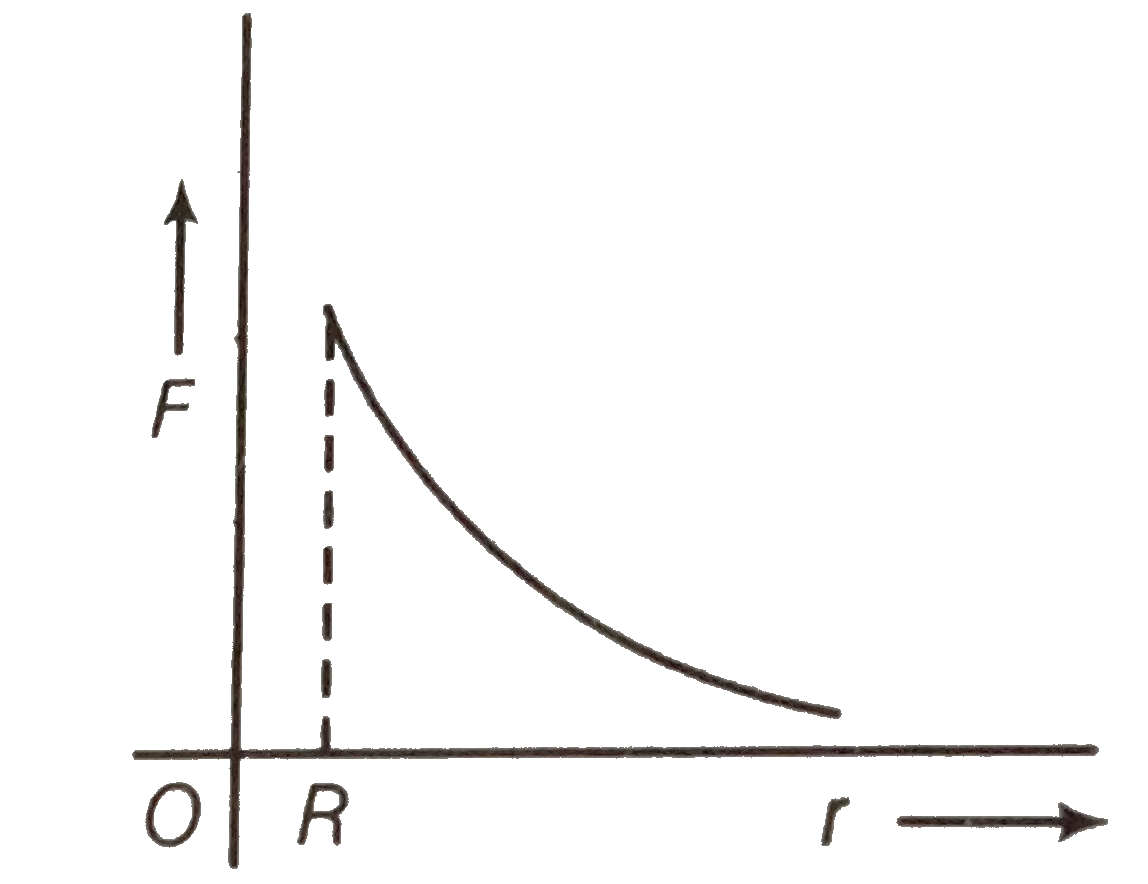
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-GRAVITATION-Very short Answer type question
- Moelcules in air in the atmosphere are attracted by gravitational forc...
Text Solution
|
- Give one example each of central and non-central force.
Text Solution
|
- Draw areal velocity time graph for Mars.
Text Solution
|
- What is the direction of areal velocity of the earth around the sun?
Text Solution
|
- How is the gravitational force between two point masses affected when ...
Text Solution
|
- Is it possible for a body to have inertia but no weight?
Text Solution
|
- We can shield a charge from electric fields by putting it inside a hol...
Text Solution
|
- An astronaut inside a small spaceship orbitting around the earth canno...
Text Solution
|
- The gravitational force between a hollow spherical shell (of radius R ...
Text Solution
|
- Out of aphelion and perihelion, where is the speed of the earth more a...
Text Solution
|
- What is the angle between the equatorial plane and the orbital plane o...
Text Solution
|